5.13 Infective Endocarditis
Overview
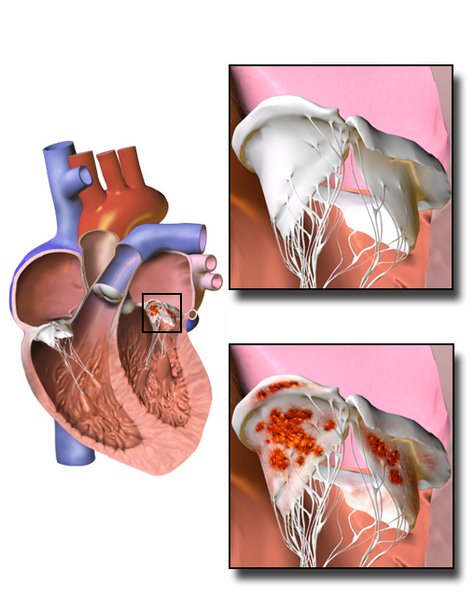
Infective endocarditis (IE) is an infection of the inner lining of the heart chambers and valves caused by bacteria or fungi. IE can lead to the formation of vegetations (clumps of infected material) on heart valves, causing damage to the valves that can impair cardiac function. Risk factors for IE include congenital heart disease, prosthetic heart valves, intravenous drug use, and dental procedures that result in transmission of bacteria into the bloodstream.[1] See Figure 5.35[2] for an illustration of IE.
Assessment
Physical assessment findings for infective endocarditis (IE) can vary depending on the stage of the infection, causative microorganism, and the presence of complications. See Table 5.13 for potential clinical manifestations of IE.
Table 5.13. Potential Clinical Manifestations of Infective Endocarditis[3],[4]
| Body System | Description |
|---|---|
| Cardiovascular | – New or changing heart murmurs (indicating valve involvement)
– Tachycardia (elevated heart rate) – Irregular heart rhythms (arrhythmias) – New signs of heart failure |
| Neurological | – Altered mental status
– Weakness, numbness, paralysis, or slurred speech |
| Respiratory | – Dyspnea
– Cough, fever, or respiratory distress |
| Integumentary | – Petechiae (small, red or purple spots)
– Splinter hemorrhages (linear hemorrhages under nails) – Osler's nodes (tender subcutaneous nodules, often on fingertips) – Janeway lesions (nontender, red or hemorrhagic macules, often on palms or soles) – Roth spots (retinal hemorrhages; visible on fundoscopy) |
| General | – Fever, chills, night sweats, fatigue, joint pain |
Diagnostic Testing`
The diagnosis of infective endocarditis (IE) typically involves a combination of clinical evaluation, laboratory tests, and imaging studies. These tests help confirm the presence of IE, identify the causative microorganism, and guide treatment.[5],[6]
- Blood cultures are collected from individuals suspected of having IE to identify the causative microorganism.
- Echocardiography is also used to examine cardiac structures and look for the presence of vegetation on heart values.
- Complete blood cell count and C-reactive protein blood tests may be used to detect systemic infection and inflammation.
Nursing Diagnoses
Nursing diagnoses for clients with infective endocarditis guide nursing care. Examples of common nursing diagnoses are the following:
- Risk for Decreased Cardiac Output
- Risk for Infection
- Risk for Decreased Tissue Perfusion
Outcome Identification
Outcome identification involves setting short- and long-term goals and creating expected outcome statements tailored to the client’s specific needs. These outcomes should be measurable and responsive to nursing interventions.
- The client will maintain cardiac output within normal limits as evidenced by systolic blood pressure in normal range.
- The client will remain free from sepsis.
- The client will maintain effective tissue perfusion as evidenced by capillary refill less than three seconds.
Interventions
Medical Interventions
Medical interventions for infective endocarditis aim to effectively resolve the infection and kill the causative microorganism.
Medication Therapy
Antibiotics are the cornerstone of treatment for IE. They are typically administered intravenously for several weeks to eradicate the infecting microorganism.
Surgical Intervention
Surgeries (such as valve repair, valve replacement, or debridement of the lesion) address complications of IE and remove infected tissue.[7],[8]
Nursing Interventions
Nursing interventions focus on safely administering prescribed medications, monitoring for complications, and managing pain. Nurses closely monitor for complications such as embolic events caused by vegetation, acute heart failure, and sepsis. Prescribed analgesics are safely administered if IE causes pain in locations such as the chest and joints. Nurses provide health teaching regarding the purpose of prescribed medications and signs of complications to promptly report to the health care provider.
Evaluation
During the evaluation stage, nurses determine the effectiveness of nursing interventions for a specific client. The previously identified expected outcomes are reviewed to determine if they were met, partially met, or not met by the time frames indicated. If outcomes are not met or only partially met by the time frame indicated, the nursing care plan is revised. Evaluation should occur every time the nurse implements interventions with a client, reviews updated laboratory or diagnostic test results, or discusses the care plan with other members of the interprofessional team.
![]() RN Recap: Infective Endocarditis
RN Recap: Infective Endocarditis
View a brief YouTube video overview of infective endocarditis[9]:
- Wang, A., & Holland, T. L. (2023). Overview of management of infective endocarditis in adults. UpToDate. https://www.uptodate.com/ ↵
- "Endocarditis.png” by BruceBlaus is licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0 ↵
- Wang, A., & Holland, T. L. (2023). Overview of management of infective endocarditis in adults. UpToDate. https://www.uptodate.com/ ↵
- Spelman, D. (2022). Complications and outcome of infective endocarditis. UpToDate. https://www.uptodate.com/ ↵
- Wang, A., & Holland, T. L. (2023). Overview of management of infective endocarditis in adults. UpToDate. https://www.uptodate.com/ ↵
- Spelman, D. (2022). Complications and outcome of infective endocarditis. UpToDate. https://www.uptodate.com/ ↵
- Wang, A., & Holland, T. L. (2023). Overview of management of infective endocarditis in adults. UpToDate. https://www.uptodate.com/ ↵
- Spelman, D. (2022). Complications and outcome of infective endocarditis. UpToDate. https://www.uptodate.com/ ↵
- Open RN Project. (2024, June 23). Health Alterations - Chapter 5 - Infective endocarditis [Video]. You Tube. CC BY-NC 4.0 https://youtu.be/uOYsbEc_Wgk?si=aN9MuN30wMtmYi7q ↵
An infection of the inner lining of the heart chambers and valves caused by bacteria or fungi.
Linear hemorrhages under nails.
Tender subcutaneous nodules.
Nontender, red or hemorrhagic macules, often on palms or soles
Retinal hemorrhages.

