1.9 Prioritization Strategies
Prioritization Strategies
Prioritization is the ability to assess a client or a group of clients and determine what is critical, what is important, and what is time-sensitive to establish a preferential order of nursing actions. Prioritization plays a crucial role in allowing nurses to navigate the multitude of demands and responsibilities they face in the health care setting. Without effective prioritization strategies, nurses can become overwhelmed by the constant time pressures and competing tasks, leading to feelings of frustration, inadequacy, and burnout. Furthermore, time scarcity can have serious consequences for client safety, as rushed or missed nursing activities can result in adverse events and increased mortality rates. By implementing appropriate prioritization strategies, nurses can better manage their time and ensure that critical interventions are addressed promptly, thus enhancing client outcomes and reducing the risk of errors.
Prioritization also impacts client satisfaction and ultimately the reimbursement levels provided by Medicare, Medicaid, and insurance companies to health care institutions. Missed or rushed nursing activities due to poor prioritization can negatively affect client satisfaction scores. By effectively prioritizing care for the nursing team, nurse leaders can improve client satisfaction, strengthen the institution’s financial standing, and contribute to overall quality improvement efforts.
Developing the skill of prioritization is an ongoing process that requires continuous learning and experience. Prioritization frameworks provide nurses with a structured approach to identifying priority client problems and implementing appropriate interventions. By understanding and utilizing these frameworks, nurses can better manage the complexity of the health care environment and make informed decisions about allocating their time and resources. Through education and practice, nurses can enhance their ability to prioritize effectively, ultimately improving client outcomes and their own professional satisfaction.
Prioritizing care is a management skill performed by nurses providing direct client care to their assigned clients, as well as by charge nurses prioritizing care for a group of clients across the nursing team. Staff nurses determine the order in which each of their assigned clients should be assessed and their needs addressed. Charge nurses assign and prioritize client care across the nursing team based on acuity and urgency while also reassigning care throughout the shift as client needs change. This skill requires the ability to assess and analyze the ever-changing clinical situation, allocate nursing team resources appropriately as client needs change, and make sound clinical decisions in a fast-paced environment. In this manner, effective prioritization across the nursing team ensures that each client receives safe, timely, and quality care, thus minimizing potential risks and complications and also distributing the workload across the nursing team equitably.
Prioritization of care for multiple clients while also performing daily nursing tasks can feel overwhelming in today’s fast-paced health care system. Because of the rapid and ever-changing conditions of clients and the structure of one’s workday, nurses must use organizational frameworks to prioritize actions and interventions. These frameworks can help ease anxiety, enhance personal organization and confidence, and ensure client safety. A variety of prioritization frameworks will be discussed in this section.
Acuity
Acuity and intensity are foundational concepts for prioritizing nursing care and interventions. Acuity refers to the level of client care that is required based on the severity of a client’s illness or condition. For example, acuity may include characteristics such as unstable vital signs, oxygenation therapy, high-risk IV medications, multiple drainage devices, or uncontrolled pain. A “high-acuity” client requires several nursing interventions and frequent nursing assessments.
Intensity addresses the time needed to complete nursing care and interventions such as providing assistance with activities of daily living (ADLs), performing wound care, or administering several medication passes. For example, a “high-intensity” client generally requires frequent or long periods of psychosocial, educational, or hygiene care from nursing staff members. High-intensity clients may also have increased needs for safety monitoring, familial support, or other needs.[1]
Many health care organizations structure their staffing assignments based on acuity and intensity ratings to help provide equity in staff assignments. Acuity helps to ensure that nursing care is strategically divided among nursing staff. An equitable assignment of clients benefits both the nurse and the client by helping to ensure that care needs do not overwhelm nursing staff, and safe, quality care is provided.
Organizations use a variety of systems when determining client acuity with rating scales based on nursing care delivery, client stability, and care needs. See an example of a client acuity tool published in the American Nurse in Table 1.9.[2] In this example, ratings range from 1 to 4, with a rating of 1 indicating a relatively stable client requiring minimal individualized nursing care and intervention. A rating of 2 reflects a client with a moderate risk who may require more frequent intervention or assessment. A rating of 3 is attributed to a complex client who requires frequent intervention and assessment. This client might also be a new admission or someone who is confused and requires more direct observation. A rating of 4 reflects a high-risk client. For example, this individual may be experiencing frequent changes in vital signs, may require complex interventions such as the administration of blood transfusions, or may be experiencing significant uncontrolled pain. An individual with a rating of 4 requires more direct nursing care and intervention than a client with a rating of 1 or 2.[3]
Table 1.9. Example of an Acuity Tool[4]
| 1: Stable Client | 2: Moderate-Risk Client | 3: Complex Client | 4: High-Risk Client | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Assessment |
|
|
|
|
| Respiratory |
|
|
|
|
| Cardiac |
|
|
|
|
| Medications |
|
|
|
|
| Drainage Devices |
|
|
|
|
| Pain Management |
|
|
|
|
| Admit/Transfer/Discharge |
|
|
|
|
| ADLs and Isolation |
|
|
|
|
| Client Score | Most = 1 | Two or > = 2 | Any = 3 | Any = 4 |
Read more about using an acuity tool on a medical-surgical unit.
Rating scales may vary among institutions, but the principles of the rating system remain the same. Organizations include various client care elements when constructing their staffing plans for each unit. Read more information about staffing models and acuity in the following box.
Staffing Models and Acuity
Organizations that base staffing on acuity systems attempt to equitably assign clients to nursing staff according to their acuity ratings. This means that when comparing client assignments across nurses on a unit, similar acuity team scores should be seen with the goal of achieving equitable and safe division of workload across the nursing team. For example, one nurse should not have a total acuity score of 6 for their client assignments while another nurse has a score of 15. If this situation occurred, the variation in scoring reflects a discrepancy in workload balance and would likely be perceived by nursing peers as unfair. Using acuity-rating staffing models is helpful to reflect the individualized nursing care required by different clients.
Alternatively, nurse staffing models may be determined by staffing ratio. Ratio-based staffing models are more straightforward in nature, where each nurse or UAP is assigned care for a set number of clients during their shift. Ratio-based staffing models may be useful for administrators creating budget requests based on the number of staff required for client care but can lead to an inequitable division of work across the nursing team when client acuity is not considered. Increasingly complex clients require more time and interventions than others, so a blend of both ratio and acuity-based staffing is helpful when determining staffing assignments.[5]
As a practicing nurse, you will be oriented to the elements of acuity ratings within your health care organization, but it is also important to understand how you can use these acuity ratings for your own prioritization and task delineation. Let’s consider the Scenario A in the following box to better understand how acuity ratings can be useful for prioritizing nursing care.
Scenario A
You report to work at 6 a.m. for your nursing shift on a busy medical-surgical unit. Prior to receiving the handoff report from your night shift nursing colleagues, you review the unit staffing grid and see that you have been assigned to four clients to start your day. The clients have the following acuity ratings:
Client A: 45-year-old client with paraplegia admitted for an infected sacral wound, with an acuity rating of 4.
Client B: 87-year-old client with pneumonia with a low-grade fever of 99.7 F and receiving oxygen at 2 L/minute via nasal cannula, with an acuity rating of 2.
Client C: 63-year-old client who is postoperative Day 1 from a right total hip replacement and is receiving pain management via a PCA pump, with an acuity rating of 2.
Client D: 83-year-old client admitted with a UTI who is finishing an IV antibiotic cycle and will be discharged home today, with an acuity rating of 1.
Based on the acuity rating system, your client assignment load receives an overall acuity score of 9. Consider how you might use their acuity ratings to help you prioritize your care. Based on what is known about the clients related to their acuity rating, whom might you identify as your care priority? Although this can feel like a challenging question to answer because of the many unknown elements in the situation using acuity numbers alone, Client A with an acuity rating of 4 would be identified as the care priority requiring assessment early in your shift.
Although acuity can be a useful tool for determining care priorities, it is important to recognize the limitations of this tool and consider how other client needs impact prioritization.
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
A second prioritization framework is Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs. When thinking back to your first nursing or psychology course, you may recall a historical theory of human motivation based on various levels of human needs called Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs. Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs reflects foundational human needs with progressive steps moving towards higher levels of achievement. This hierarchy of needs is traditionally represented as a pyramid with the base of the pyramid serving as essential needs that must be addressed before one can progress to another area of need.[6] See Figure 1.5[7] for an illustration of Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs.
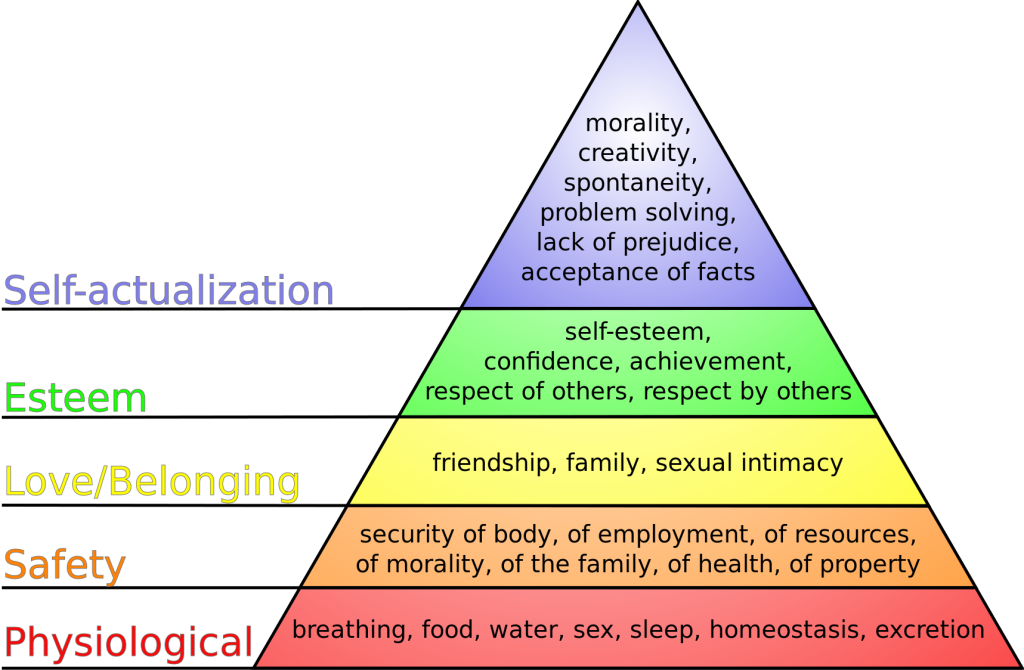
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs places physiological needs as the foundational base of the pyramid.[8] Physiological needs include oxygen, food, water, sex, sleep, homeostasis, and excretion. The second level of Maslow’s hierarchy reflects safety needs. Safety needs include elements that keep individuals safe from harm. An example of safety needs in health care includes fall precautions. The third level of Maslow’s hierarchy reflects emotional needs such as love and a sense of belonging. These needs are often reflected in an individual’s relationships with family members and friends. The top two levels of Maslow’s hierarchy include esteem and self-actualization. An example of addressing these needs in a health care setting is helping an individual build self-confidence in performing blood glucose checks that leads to improved self-management of their diabetes.
So how does Maslow’s theory impact prioritization? To better understand the application of Maslow’s theory to prioritization, consider Scenario B in the following box.
Scenario B
You are an emergency response nurse working at a local shelter in a community that has suffered a devastating hurricane. Many individuals have relocated to the shelter for safety in the aftermath of the hurricane. Much of the community is still without electricity and clean water, and many homes have been destroyed. You approach a young woman who has a laceration on her scalp that is bleeding through her gauze dressing. The woman is weeping as she describes the loss of her home stating, “I have lost everything! I just don’t know what I am going to do now. It has been a day since I have had water or anything to drink. I don’t know where my sister is, and I can’t reach any of my family to find out if they are okay!”
Despite this relatively brief interaction, this woman has shared with you a variety of needs. She has demonstrated a need for food, water, shelter, homeostasis, and family. As the nurse caring for her, it might be challenging to think about where to begin her care. These thoughts could be racing through your mind:
Should I begin to make phone calls to try and find her family? Maybe then she would be able to calm down.
Should I get her on the list for the homeless shelter so she wouldn’t have to worry about where she will sleep tonight?
She hasn’t eaten in a while; I should probably find her something to eat.
All these needs are important and should be addressed at some point, but Maslow’s hierarchy provides guidance on what needs must be addressed first. Use the foundational level of Maslow’s pyramid of physiological needs as the top priority for care. The woman is bleeding heavily from a head wound and has had limited fluid intake. As the nurse caring for this client, it is important to immediately intervene to stop the bleeding and restore fluid volume. Stabilizing the client by addressing her physiological needs is required before undertaking additional measures such as contacting her family. Imagine if instead you made phone calls to find the client’s family and didn’t address the bleeding or dehydration – you might return to a severely hypovolemic client who has deteriorated and may be near death. In this example, prioritizing emotional needs above physiological needs can lead to significant harm to the client.
Although this is a relatively straightforward example, the principles behind the application of Maslow’s hierarchy are essential. Addressing physiological needs before progressing toward additional need categories concentrates efforts on the most vital elements to enhance client well-being. Maslow’s hierarchy provides the nurse with a helpful framework for identifying and prioritizing critical client care needs.
ABCs
Airway, breathing, and circulation, otherwise known by the mnemonic “ABCs,” is another prioritization framework that assists nurses in prioritization. Like Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs framework, using the ABCs guides nursing decision-making based on the most critical needs for preserving human life. If a client does not have a patent airway, is unable to breathe, or has inadequate circulation, very little of what else we do matters. The client’s ABCs are reflected in Maslow’s foundational level of physiological needs and direct critical nursing actions and timely interventions. Let’s consider Scenario C in the following box regarding prioritization using the ABCs and the physiological base of Maslow’s hierarchy.
Scenario C
You are a nurse on a busy cardiac floor charting your morning assessments on a computer at the nurses’ station. Down the hall from where you are charting, two of your assigned clients are resting comfortably in Room 504 and Room 506. Suddenly, both call lights ring from the rooms, and you answer them via the intercom at the nurses’ station.
Room 504 has an 87-year-old male who has been admitted with heart failure, weakness, and confusion. He has a bed alarm for safety and has been ringing his call bell for assistance appropriately throughout the shift. He requires assistance to get out of bed to use the bathroom. He received his morning medications, which included a diuretic about 30 minutes previously, and now reports significant urge to void and needs assistance to the bathroom.
Room 506 has a 47-year-old woman who was hospitalized with new onset atrial fibrillation with rapid ventricular response. The client underwent a cardioversion procedure yesterday that resulted in successful conversion of her heart back into normal sinus rhythm. She is reporting via the intercom that her “heart feels as though it is doing that fluttering thing again,” and she is having chest pain with breathlessness.
Based upon these two client scenarios, it might be difficult to determine whom you should see first. Both clients are demonstrating needs in the foundational physiological level of Maslow’s hierarchy and require assistance. To prioritize between these clients’ physiological needs, the nurse can apply the principles of the ABCs to determine intervention. The client in Room 506 reports both breathing and circulation issues, warning indicators that action is needed immediately. Although the client in Room 504 also has an urgent physiological elimination need, it does not overtake the critical one experienced by the client in Room 506. The nurse should immediately assess the client in Room 506 while also calling for assistance from a team member to assist the client in Room 504.
CURE
Prioritizing what should be done and when it can be done can be a challenging task when several clients all have physiological needs. Recently, there has been professional acknowledgement of the cognitive challenge for novice nurses in differentiating these physiological needs. To expand on the principles of prioritizing using the ABCs, the CURE hierarchy has been introduced to help novice nurses better understand how to manage competing client needs. The CURE hierarchy uses the acronym “CURE” to guide prioritization based on identifying the differences among Critical needs, Urgent needs, Routine needs, and Extras.[9]
“Critical” client needs require immediate action. Examples of critical needs align with the ABCs and Maslow’s physiological needs, such as symptoms of respiratory distress, chest pain, and airway compromise. No matter the complexity of their shift, nurses can be assured that addressing clients’ critical needs is the correct prioritization of their time and energies.
After critical client care needs have been addressed, nurses can then address “urgent” needs. Urgent needs are characterized as needs that cause client discomfort or place the client at a significant safety risk.[10]
The third part of the CURE hierarchy reflects “routine” client needs. Routine client needs can also be characterized as “typical daily nursing care” because the majority of a standard nursing shift is spent addressing routine client needs. Examples of routine daily nursing care include actions such as administering medication and performing physical assessments.[11] Although a nurse’s typical shift in a hospital setting includes these routine client needs, they do not supersede critical or urgent client needs.
The final component of the CURE hierarchy is known as “extras.” Extras refer to activities performed in the care setting to facilitate client comfort but are not essential.[12] Examples of extra activities include providing a massage for comfort or washing a client’s hair. If a nurse has sufficient time to perform extra activities, they contribute to a client’s feeling of satisfaction regarding their care, but these activities are not essential to achieve client outcomes.
Let’s apply the CURE mnemonic to client care in the following box.
If we return to Scenario C regarding clients in Room 504 and 506, we can see the client in Room 504 is having urgent needs. He is experiencing a physiological need to urgently use the restroom and may also have safety concerns if he does not receive assistance and attempts to get up on his own because of weakness. He is on a bed alarm, which reflects safety considerations related to his potential to get out of bed without assistance. Despite these urgent indicators, the client in Room 506 is experiencing a critical need and takes priority. Recall that critical needs require immediate nursing action to prevent client deterioration. The client in Room 506 with a rapid, fluttering heartbeat and shortness of breath has a critical need because without prompt assessment and intervention, their condition could rapidly decline and become fatal.
Data Cues
In addition to using the previously identified frameworks and tools to assist with priority setting, nurses must also look at their clients’ data cues to help them identify care priorities. Data cues are pieces of significant clinical information that direct the nurse toward a potential clinical concern or a change in condition. For example, have the client’s vital signs worsened over the last few hours? Is there a new laboratory result that is concerning? Data cues are used in conjunction with prioritization frameworks to help the nurse holistically understand the client’s current status and where nursing interventions should be directed. Common categories of data clues include acute versus chronic conditions, actual versus potential problems, unexpected versus expected conditions, information obtained from the review of a client’s chart, and diagnostic information.
Acute Versus Chronic Conditions
A common data cue that nurses use to prioritize care is considering if a condition or symptom is acute or chronic. Acute conditions have a sudden and severe onset. These conditions occur due to a sudden illness or injury, and the body often has a significant response as it attempts to adapt. Chronic conditions have a slow onset and may gradually worsen over time. The difference between an acute versus a chronic condition relates to the body’s adaptation response. Individuals with chronic conditions often experience less symptom exacerbation because their body has had time to adjust to the illness or injury. Let’s consider an example of two clients admitted to the medical-surgical unit complaining of pain in Scenario D in the following box.
Scenario D
As part of your client assignment on a medical-surgical unit, you are caring for two clients who both ring the call light and report pain at the start of the shift. Client A was recently admitted with acute appendicitis, and Client B was admitted for observation due to osteoarthritis. Not knowing any additional details about the clients’ conditions or current symptoms, which client would receive priority in your assessment? Based on using the data cue of acute versus chronic conditions, Client A with a diagnosis of acute appendicitis would receive top priority for assessment over a client with chronic pain due to osteoarthritis. Clients experiencing acute pain require immediate nursing assessment and intervention because it can indicate a change in condition. Acute pain also elicits physiological effects related to the stress response, such as elevated heart rate, blood pressure, and respiratory rate, and should be addressed quickly.
Actual Versus Potential Problems
Nursing diagnoses and the nursing care plan have significant roles in prioritization when interpreting assessment data cues. Actual problems refer to a clinical problem that is actively occurring with the client. A potential problem indicates the client may potentially experience a problem, but they do not have current signs or symptoms of the problem actively occurring.
Consider an example of prioritizing actual and potential problems in Scenario E in the following box.
Scenario E
A 74-year-old woman with a previous history of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is admitted to the hospital for pneumonia. She has generalized weakness, a weak cough, and crackles in the bases of her lungs. She is receiving IV antibiotics, fluids, and oxygen therapy. The client can sit at the side of the bed and ambulate with the assistance of staff, although she requires significant encouragement to ambulate.
Nursing diagnoses are established for this client as part of the care planning process. One nursing diagnosis for this client is Ineffective Airway Clearance. This nursing diagnosis is an actual problem because the client is currently exhibiting signs of poor airway clearance with an ineffective cough and crackles in the lungs. Nursing interventions related to this diagnosis include coughing and deep breathing, administering nebulizer treatments, and evaluating the effectiveness of oxygen therapy. The client also has the nursing diagnosis Risk for Skin Breakdown based on her weakness and lack of motivation to ambulate. Nursing interventions related to this diagnosis include repositioning every two hours and assisting with ambulation twice daily.
The established nursing diagnoses provide cues for prioritizing care. For example, if the nurse enters the client’s room and discovers the client is experiencing increased shortness of breath, nursing interventions to improve the client’s respiratory status receive top priority before attempting to get the client to ambulate.
Although there may be times when risk problems may supersede actual problems, looking to the “actual” nursing problems can provide clues to assist with prioritization.
Unexpected Versus Expected Conditions
In a similar manner to using acute versus chronic conditions as a cue for prioritization, it is also important to consider if a client’s signs and symptoms are “expected” or “unexpected” based on their overall condition. Unexpected conditions are findings that are not likely to occur in the normal progression of an illness, disease, or injury. Expected conditions are findings that are likely to occur or are anticipated in the course of an illness, disease, or injury. Unexpected findings often require immediate action by the nurse.
Let’s apply this tool to the two clients previously discussed in Scenario D. As you recall, both Client A (with acute appendicitis) and Client B (with weakness and diagnosed with osteoarthritis) are reporting pain. Acute pain typically receives priority over chronic pain. But what if both clients are also reporting nausea and have an elevated temperature? Although these symptoms must be addressed in both clients, they are “expected” symptoms with acute appendicitis (and typically addressed in the treatment plan) but are “unexpected” for the client with osteoarthritis. Critical thinking alerts you to the unexpected nature of these symptoms in Client B, so they receive priority for assessment and nursing interventions.
Handoff Report/Chart Review
Additional data cues that are helpful in guiding prioritization come from information obtained during a handoff nursing report and review of the client’s chart. These data cues can be used to establish a client’s baseline status and prioritize new clinical concerns based on abnormal assessment findings. Let’s consider Scenario F in the following box based on cues from a handoff report and how it might be used to help prioritize nursing care.
Scenario F
Imagine you are receiving the following handoff report from the night shift nurse for a client admitted to the medical-surgical unit with pneumonia:
At the beginning of my shift, the client was on room air with an oxygen saturation of 93%. She had slight crackles in both of her posterior lungs. At 0530, the client rang the call light to go to the bathroom. As I escorted her to the bathroom, she appeared slightly short of breath. Upon returning the client to bed, I rechecked her vital signs and found her oxygen saturation at 88% on room air and respiratory rate of 20. I listened to her lung sounds and noticed more persistent crackles and coarseness than at bedtime. I placed the client on 2 L/minute of oxygen via nasal cannula. Within 5 minutes, her oxygen saturation increased to 92%, and she reported increased ease in respiration.
Based on the handoff report, the night shift nurse provided substantial clinical evidence that the client may be experiencing a change in condition. Although these changes could be attributed to lack of lung expansion that occurred while the client was sleeping, there is enough information to indicate to the oncoming nurse that follow-up assessment and interventions should be prioritized for this client because of potentially worsening respiratory status. In this manner, identifying data cues from a handoff report can assist with prioritization.
Now imagine the night shift nurse had not reported this information during the handoff report. Is there another method for identifying potential changes in client condition? Many nurses develop a habit of reviewing their clients’ charts at the start of every shift to identify trends and “baselines” in client condition. For example, a chart review reveals a client’s heart rate on admission was 105 beats per minute. If the client continues to have a heart rate in the low 100s, the nurse is not likely to be concerned if today’s vital signs reveal a heart rate in the low 100s. Conversely, if a client’s heart rate on admission was in the 60s and has remained in the 60s throughout their hospitalization, but it is now in the 100s, this finding is an important cue requiring prioritized assessment and intervention.
Diagnostic Information
Diagnostic results are also important when prioritizing care. In fact, the National Patient Safety Goals from The Joint Commission include prompt reporting of important test results. Newly reported abnormal results may indicate a client’s change in condition. They are typically flagged in a client’s chart or are reported directly by phone to the nurse by the laboratory as they become available. For example, a hemoglobin level of 5 mg/dL or new infiltrates on a chest X-ray should be reported to the provider and may require additional nursing interventions. Let’s consider Scenario G in which you are the nurse providing care for five medical-surgical clients.
Scenario G
You completed morning assessments on your assigned five clients. Client A previously underwent a total right knee replacement and will be discharged home today. You are about to enter Client A’s room to begin discharge teaching when you receive a phone call from the laboratory department, reporting a critical hemoglobin of 6.9 gm/dL on Client B. Rather than enter Client A’s room to perform discharge teaching, you immediately reprioritize your care. You call the primary provider to report Client B’s critical hemoglobin level and determine if additional intervention, such as a blood transfusion, is required.
- Oregon Health Authority. (2021, April 29). Hospital nurse staffing interpretive guidance on staffing for acuity & intensity. Public Health Division, Center for Health Protection. https://www.oregon.gov/oha/PH/PROVIDERPARTNERRESOURCES/HEALTHCAREPROVIDERSFACILITIES/HEALTHCAREHEALTHCAREREGULATIONQUALITYIMPROVEMENT/Documents/NSInterpretiveGuidanceAcuity.pdf ↵
- Ingram, A., & Powell, J. (2018). Patient acuity tool on a medical surgical unit. American Nurse. https://www.myamericannurse.com/patient-acuity-medical-surgical-unit/ ↵
- Kidd, M., Grove, K., Kaiser, M., Swoboda, B., & Taylor, A. (2014). A new patient-acuity tool promotes equitable nurse-patient assignments. American Nurse Today, 9(3), 1-4. https://www.myamericannurse.com/a-new-patient-acuity-tool-promotes-equitable-nurse-patient-assignments/ ↵
- Ingram, A., & Powell, J. (2018). Patient acuity tool on a medical surgical unit. American Nurse. https://www.myamericannurse.com/patient-acuity-medical-surgical-unit/ ↵
- Welton, J. M. (2017). Measuring patient acuity. JONA: The Journal of Nursing Administration, 47(10), 471. https://doi.org/10.1097/nna.0000000000000516 ↵
- Maslow, A. H. (1943). A theory of human motivation. Psychological Review, 50(4), 370–396. https://doi.org/10.1037/h0054346 ↵
- “Maslow's_hierarchy_of_needs.svg” by J. Finkelstein is licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0 ↵
- Stoyanov, S. (2017). An analysis of Abraham Maslow's A Theory of Human Motivation (1st ed.). Routledge. https://doi.org/10.4324/9781912282517 ↵
- Kohtz, C., Gowda, C., & Guede, P. (2017). Cognitive stacking: Strategies for the busy RN. Nursing2021, 47(1), 18-20. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.nurse.0000510758.31326.92 ↵
- Kohtz, C., Gowda, C., & Guede, P. (2017). Cognitive stacking: Strategies for the busy RN. Nursing2021, 47(1), 18-20. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.nurse.0000510758.31326.92 ↵
- Kohtz, C., Gowda, C., & Guede, P. (2017). Cognitive stacking: Strategies for the busy RN. Nursing2021, 47(1), 18-20. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.nurse.0000510758.31326.92 ↵
- Kohtz, C., Gowda, C., & Guede, P. (2017). Cognitive stacking: Strategies for the busy RN. Nursing2021, 47(1), 18-20. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.nurse.0000510758.31326.92 ↵
The ability to assess a client or a group of clients and determine what is critical, what is important, and what is time-sensitive to establish a preferential order of nursing actions.
The level of client care that is required based on the severity of a client’s illness or condition
The time needed to complete nursing care and interventions such as providing assistance with activities of daily living (ADLs), performing wound care, or administering several medication passes
Staffing model in which accounts for the individualized nursing care required by different clients
Useful for administrators creating budget requests based on the number of staff required for client care

