2.3 Body Cavities
Body Cavities
The body maintains its internal organization by membranes and other structures that separate compartments. The dorsal (posterior) cavity and the ventral (anterior) cavity are the largest compartments of the body, as shown in Figure 2.3.[1] The dorsal (posterior) cavity includes the cranial and spinal (vertebral) cavities. The ventral (anterior) cavity includes the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities.
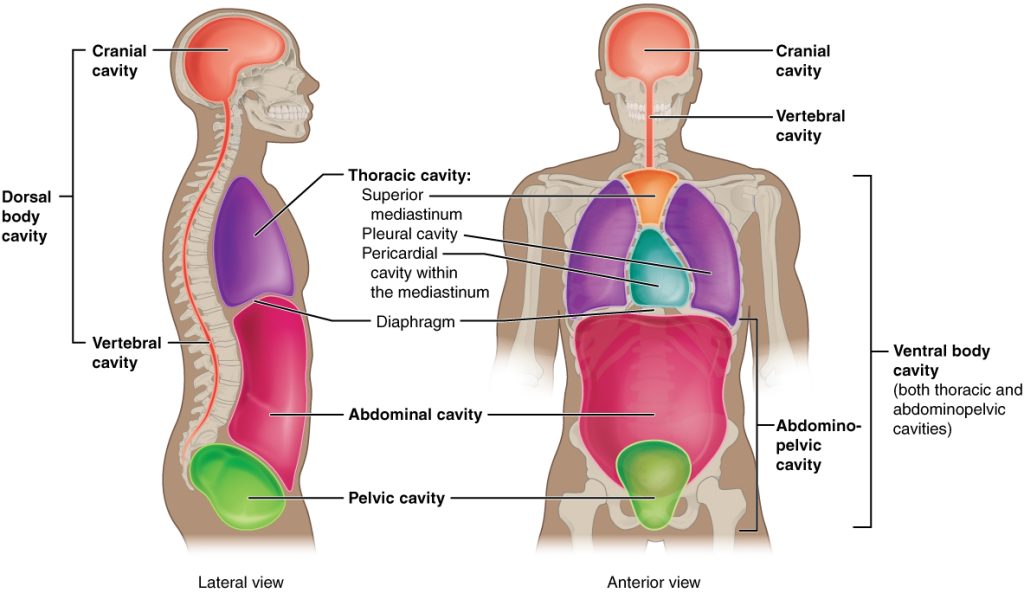
In the dorsal cavity, the cranial cavity houses the brain. The brain is protected by the bones of the skulls and the cerebrospinal fluid. The spinal cavity (vertebral cavity) encloses the spinal cord. It is protected by the vertebral column and cerebrospinal fluid. In the ventral cavity, the thoracic cavity is superior in position to the abdominopelvic cavity, and it is enclosed by the rib cage. The thoracic cavity contains the lungs and the heart. The diaphragm forms the floor of the thoracic cavity and separates it from the abdominopelvic cavity. The abdominopelvic cavity is the largest cavity in the body. The abdominopelvic cavity houses the digestive organs, the pelvic cavity, and the reproductive organs. The ventral cavity also allows for significant changes in the size and shape of the organs as they perform their functions. For example, the lungs, heart, stomach, and intestines can expand and contract without distorting other tissues or disrupting the activity of nearby organs.
View a supplementary YouTube video[2] on body cavities and membranes:
- “Dorsal_Ventral_Body_Cavities.jpg” by OpenStax is licensed under CC BY 4.0. Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/anatomy-and-physiology-2e/pages/1-introduction ↵
- RegisteredNurseRN. (2019, June 12). Body cavities and membranes (Dorsal, Ventral) - Anatomy and physiology [Video]. All rights reserved. Reused with permission. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4GLMjSj4k9U ↵

