16.7 Medical Specialists, Diagnostic Testing, and Procedures Related to the Nervous System
Medical Specialists
Neurology (noo-ROL-ŏ-jē) is the study of the nervous system. Psychiatry (sī-KĪ-ă-trē) is the study of disorders of the mind. Psychology (sī-KOL-ŏ-jē) is the study of the mind.
Neurologist
A neurologist (nū-RŎL-ō-jĭst) is a physician who specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of disorders and conditions related to the brain, spinal cord, nerves, and muscles. Neurosurgeons (nū-RŎ-sŭrj- ŭnz) perform surgeries on the nervous system.
Read additional information about neurologists on the American Academy of Neurology’s web page.
Psychiatrist
A psychiatrist (sī-KĪ-ă-trĭst) is a medical doctor who specializes in mental health and substance disorders. Because they are physicians, psychiatrists can order or perform a full range of medical laboratory and psychological tests. Mental health diagnoses are based on criteria established in Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5), which contains descriptions, symptoms, and other criteria for diagnosing mental disorders. Psychiatrists prescribe a variety of treatments, including talk therapy, medications, psychosocial interventions, and other treatments such as electroconvulsive therapy (ē-lek-trō-kŏn-VŬL-sĭv THĔR-ă-pē) (ECT), depending on the needs of each patient. ECT is the application of electrical currents to the brain, typically used to treat severe depression that has not responded to other treatments.
Read more information about psychiatrists on the American Psychiatric Association’s web page.
Psychologist
Psychologists (sī-KŎL-ō-jĭstz) are professionals with graduate degrees, and many have doctoral degrees (i.e., PhD, PsyD, or EdD). They specialize in helping people learn to cope with stressful situations, overcome substance use disorders, and manage chronic mental health disorders, and they also perform psychological tests.
Read more information about psychologists on the American Psychological Association’s web page.
Social Workers
Social workers (SŌ-shăl WŬR-kĕrz) help people prevent and cope with problems in their everyday lives. Social workers typically need a bachelor’s or master’s degree in social work (BSW or MSW) from an accredited program.
Read more about social workers on the Bureau of Labor Statistics’ web page.
Counselors
Substance use and mental health counselors advise people on issues such as those relating to alcoholism, substance use disorders, or depression. Education and training requirements vary for entering these occupations by state. For example, in Wisconsin there are associate degree programs available in substance use disorder counseling. Mental health counseling typically requires a master’s degree.
Read more about counselors on the Bureau of Labor Statistics’ web page.
Diagnostic Tests Related to the Nervous System
Cerebral Angiography
Cerebral angiography (SĚR-ă-brĭl, an-jē-OG-ră-fē) uses X-rays and special dye to see how blood flows through the brain. Specially trained health care providers perform this procedure in an operating room. During the procedure, a provider inserts a catheter into an artery in the wrist or groin area, injects contrast material through the catheter, and then takes X-rays of the blood vessels. Cerebral angiograms provide more detailed images of blood vessels than other imaging tests, like CT or MRI scans.[1]
Electroencephalogram (EEG)
An electroencephalogram (ĕ-lek-trō-ĕn-SEF-ă-lŏ-gram) (EEG) is a test to measure the electrical activity of the brain. The test is performed by an electroencephalogram (EEG) technologist in a laboratory, health care provider’s office, or hospital. Flat metal disks called electrodes are placed on many spots on the scalp. The electrodes are connected by wires to a recording machine that changes the electrical signals into patterns that can be seen on a monitor or drawn on paper.[2] See Figure 16.14[3] for an image of an EEG.
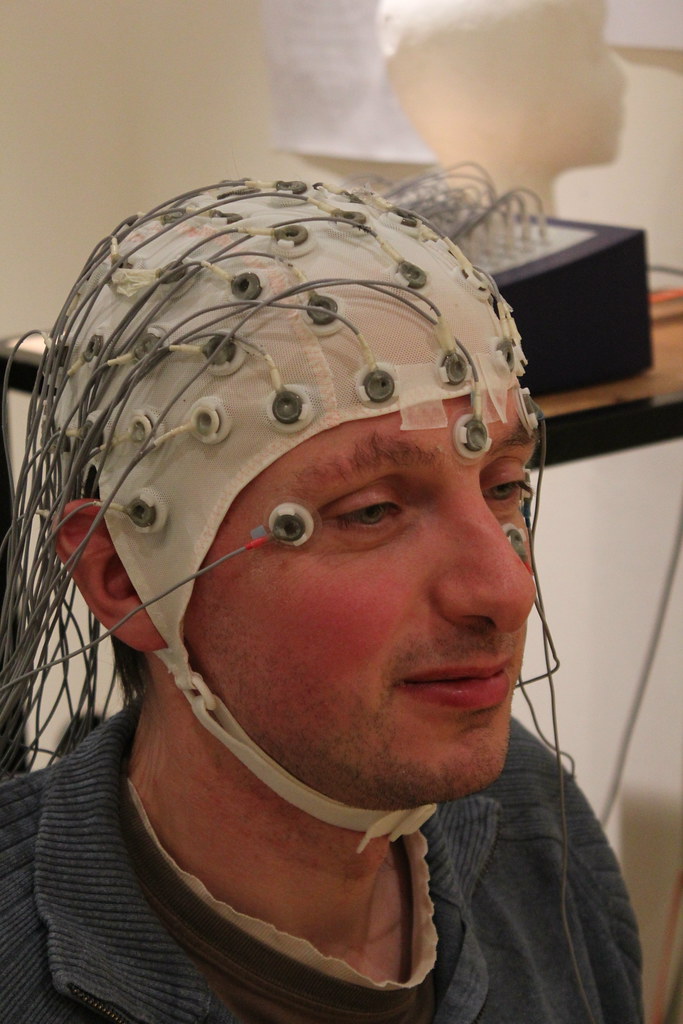
Electromyography (EMG)
An electromyogram (ē-lĕk-trō-mī-Ŏ-grăm) (EMG) is a diagnostic procedure that assesses the function of nerve cells that control muscles. Electrodes, either attached to the skin or inserted into the muscle, record electrical impulses. An EMG can identify functional problems with the peripheral nerves, muscles, or with the signals between the nerves and the muscles. A nerve conduction study, another part of an EMG, uses surface electrodes applied to the skin to measure the speed and strength of signals traveling between two or more points. EMG results are used to diagnose muscle and nerve disorders.[4]
Lumbar Puncture (Spinal Tap)
A lumbar puncture (LŬM-băr PŬNK-chŭr), which is also called a spinal tap, is a test used to diagnose nervous system infections and other conditions. During a lumbar puncture, a needle is inserted into the space between two vertebrae in the lumbar region to remove a sample of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). CSF is the fluid that surrounds the brain and spinal cord to protect them from injury.[5] See Figure 16.15[6] for an illustration of a lumbar puncture.
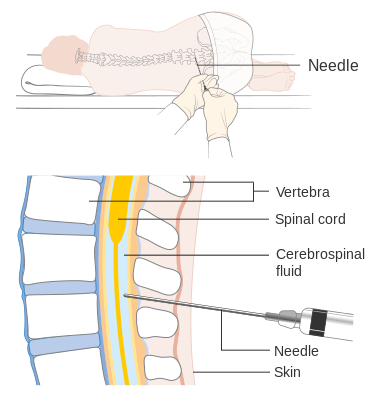
Procedures Related to the Nervous System
Carotid Endarterectomy
A carotid endarterectomy (kă-rŏt-ĭd ĕnd-ăr-tĕr-ĔK-tŏ-mē) is the surgical removal of plaque blocking the carotid arteries in the neck. The carotid arteries are the main blood vessels that carry oxygen and blood to the brain. This procedure is performed to prevent or treat a stroke.[7]
- Cleveland Clinic. (2023, August 8). Cerebral angiogram. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diagnostics/13476-cerebral-angiogram ↵
- A.D.A.M. Medical Encyclopedia [Internet]. Atlanta (GA): A.D.A.M., Inc.; c1997-2023. EEG; [reviewed 2023, Jan 1; cited 2023, Dec 7). https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/003931.htm ↵
- “Three_quarter_view_of_EEG_subject.jpg” by Chris Hope and shared by Tim Sheerman-Chase is licensed under CC BY 2.0 ↵
- Mayo Clinic. (2019, May 21). Electromyography (EMG). https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/emg/about/pac-20393913 ↵
- Mayo Clinic. (2022, April 30). Lumbar puncture (spinal tap). https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/lumbar-puncture/about/pac-20394631 ↵
- “Diagram_showing_how_you_have_a_lumbar_puncture_CRUK_157.svg” by Cancer Research UK is licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0 ↵
- Johns Hopkins Medicine. (n.d.). Carotid endarterectomy. https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/treatment-tests-and-therapies/carotid-endarterectomy ↵

