6.3 Alzheimer’s Disease
Open Resources for Nursing (Open RN)
Alzheimer’s disease is an irreversible, progressive brain disorder that slowly destroys memory and thinking skills and eventually the ability to carry out the simplest tasks. It is the most common cause of dementia. In most people with Alzheimer’s disease, symptoms first appear in their mid-60s. Five percent of people age 65 to 74, 13.2% of people age 75 to 84, and 33.4% of people age 85 or older have Alzheimer’s disease.[1]
Scientists continue to unravel the complex brain changes involved in the onset and progression of Alzheimer’s disease. Researchers have found many genes that increase or decrease the risk of Alzheimer’s dementia. In 2022 researchers identified 31 new genes that appear to affect biological processes associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Changes in the brain may begin a decade or more before memory and other cognitive problems appear. Abnormal deposits of proteins form amyloid plaques and tau tangles throughout the brain. Previously healthy neurons stop functioning, lose connections with other neurons, and die. The damage initially appears to take place in the hippocampus and cortex, the parts of the brain essential in forming memories. As more neurons die, additional parts of the brain are affected and begin to shrink. By the final stage of Alzheimer’s, damage is widespread, and brain tissue has shrunk significantly.[2],[3] See Figure 6.6[4] for an image of the changes occurring in the brain during Alzheimer’s disease.
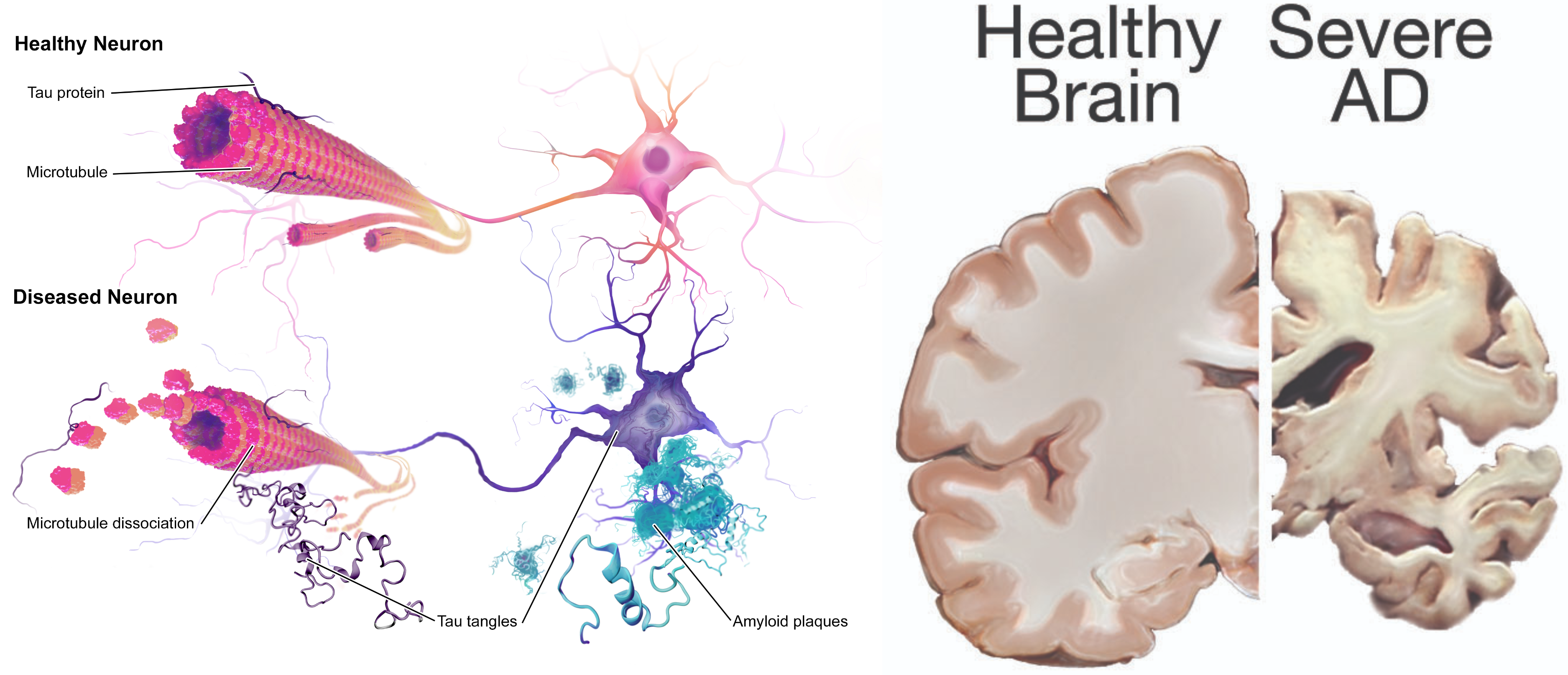
View a supplementary YouTube video of the changes that occur in the brain during Alzheimer’s disease: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hEw1Yq_4PaA[5]
Symptoms of Early Alzheimer’s Disease
There are ten symptoms of early Alzheimer’s disease[6]:
- Memory loss that disrupts daily life. This includes forgetting important dates or events, asking the same questions over and over, and increasingly needing to rely on memory aids (e.g., reminder notes or electronic devices) or family members for things they used to handle on their own. This is different than a typical age-related change of sometimes forgetting names or appointments, but remembering them later.
- Challenges in planning or solving problems. This includes changes in an individual’s ability to develop and follow a plan or work with numbers. For example, they may have trouble following a familiar recipe or keeping track of monthly bills. They may have difficulty concentrating and take much longer to do things than they did before. This is different from a typical age-related change of making occasional errors when managing finances or household bills.
- Difficulty completing familiar tasks. This includes trouble driving to a familiar location, organizing a grocery list, or remembering the rules of a favorite game. This symptom is different from a typical age-related change of occasionally needing help to use microwave settings or to record a TV show.
- Confusion with time or place. This includes losing track of dates, seasons, and the passage of time. Individuals may have trouble understanding something if it is not happening immediately. Sometimes they may forget where they are or how they got there. This symptom is different from a typical age-related change of forgetting the date or day of the week but figuring it out later.
- Trouble understanding visual images and spatial relationships. Vision problems that include difficulty judging distance, determining color or contrast, or causing issues with balance or driving can be symptoms of Alzheimer’s. This is different from a typical age-related change of blurred vision related to presbyopia or cataracts. (See the “Sensory Impairments” chapter for more information on common vision problems.)
- New problems with words in speaking or writing. Individuals with Alzheimer’s may have trouble following or joining a conversation. They may stop in the middle of a conversation and have no idea how to continue or they may repeat themselves. They may struggle with vocabulary, have trouble naming a familiar object, or use the wrong name (e.g., calling a “watch” a “hand-clock”). This is different from a typical age-related change of having trouble finding the right word.
- Misplacing things and losing the ability to retrace steps. A person with Alzheimer’s disease may put things in unusual places. They may lose things and be unable to go back over their steps to find them again. They may accuse others of stealing, especially as the disease progresses. This is different from a typical age-related change of misplacing things from time to time and retracing steps to find them.
- Decreased or poor judgment. Individuals with Alzheimer’s may experience changes in judgment or decision-making. For example, they may use poor judgment when dealing with money or pay less attention to grooming or keeping themselves clean. This is different from a typical age-related change of making a bad decision or mistake once in a while, like neglecting to change the oil in the car.
- Withdrawal from work or social activities. A person living with Alzheimer’s disease may experience changes in the ability to hold or follow a conversation. As a result, they may withdraw from hobbies, social activities, or other engagements. They may have trouble keeping up with a favorite team or activity. This is different from a typical age-related change of sometimes feeling uninterested in family or social obligations.
- Changes in mood, personality, and behavior. Individuals living with Alzheimer’s may experience mood and personality changes. They can become confused, suspicious, depressed, fearful, or anxious. They may be easily upset at home, with friends, or when out of their comfort zone. This is different from a typical age-related change of developing very specific ways of doing things and becoming irritable when a routine is disrupted.
Stages of Alzheimer’s Disease
There are several stages of Alzheimer’s disease (AD), referred to as preclinical AD, mild cognitive impairment due to AD, dementia due to mild AD, dementia due to moderate AD, and dementia due to severe AD[7]:
- Preclinical AD: Individuals experience brain changes associated with Alzheimer’s disease, but symptoms such as memory loss or difficulty thinking are not yet present.
- Mild cognitive impairment due to AD: Individuals have very mild symptoms that do not interfere with everyday activities.
- Dementia due to mild AD: Individuals experience the ten symptoms previously discussed that interfere with some daily activities. They may still be able to drive, work and participate in their favorite activities but often need more time to complete common daily tasks and may require assistance to maximize independence and remain safe. Paying bills and making financial decisions may be especially challenging, which increases their vulnerability to financial scams and financial abuse.
- Dementia due to moderate AD: Individuals experience symptoms that interfere with many daily activities. They often have difficulty completing multistep tasks such as bathing and dressing. They may have episodes of incontinence, begin to have problems recognizing loved ones, and start showing personality and behavioral changes, including suspiciousness and agitation. Behavioral symptoms such as wandering, getting lost, hallucinations, delusions, and repetitive behavior may occur. Clients living at home may engage in risky behavior, such as leaving the house in clothing inappropriate for weather conditions or leaving on the stove burners.[8]
- Dementia due to severe AD: The ability to verbally communicate and walk is greatly diminished, and individuals likely require around-the-clock care with full assistance in washing, dressing, eating, and toileting. They typically spend most of their time in a wheelchair or in bed. This loss of mobility increases their vulnerability to physical complications including blood clots, skin infections and sepsis. Swallowing becomes impaired, increasing their risk for aspiration pneumonia, a common cause of death. See Figure 6.7[9] of a client with dementia requiring assistance with dressing.

There is no single diagnostic test that can determine if a person has Alzheimer’s disease. Health care providers use a client’s medical history, mental status tests, physical and neurological exams, and diagnostic tests to diagnose Alzheimer’s disease and other types of dementia. During the neurological exam, reflexes, coordination, muscle tone and strength, eye movement, speech, and sensation are tested.
Mental status testing evaluates memory, thinking, and simple problem-solving abilities. Some tests are brief, whereas others can be more time-intensive and complex. These tests give an overall sense of whether a person is aware of their symptoms; knows the date, time, and place where they are; can remember a short list of words; and if they can follow instructions and do simple calculations. The Mini Mental Status Examination (MMSE) and Mini-Cog test are two commonly used assessments.
During the MMSE, a health professional asks a client a series of questions designed to test a range of everyday mental skills. The maximum MMSE score is 30 points. A score of 20 to 24 suggests mild dementia, 13 to 20 suggests moderate dementia, and less than 12 indicates severe dementia. On average, the MMSE score of a person with Alzheimer’s declines about two to four points each year.
During the Mini-Cog, a person is asked to complete two tasks: remember and then later repeat the names of three common objects and draw a face of a clock showing all 12 numbers in the right places with the time indicated as specified by the examiner. The results of this brief test determine if further evaluation is needed. In addition to assessing mental status, the health care provider evaluates a person’s sense of well-being to detect depression or other mood disorders that can cause memory problems, loss of interest in life, and other symptoms that can overlap with dementia.
Diagnostic testing for Alzheimer’s disease may include cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) testing for abnormal levels of beta-amyloid and tau, or positron emission tomography (PET) scans that can identify beta-amyloid and tau accumulations in the brain. Many research groups are currently working on developing blood tests for Alzheimer’s disease that could speed up the diagnosis and facilitate early treatment.[10]
Treatments
While there is no cure for Alzheimer’s disease, medications may be prescribed to slow disease progression and manage common symptomatic behaviors.
Medications
The medications aducanumab and lecanemab may be prescribed to delay disease progression by helping remove plaques and prevent the development of beta-amyloid plaques. However, in 2024 the manufacturer of aducanumab announced the drug was being discontinued. Clinical trials using lecanemab show moderate slowing of cognitive and functional decline in individuals with mild cognitive impairment or mild dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease. However, it may cause serious side effects such as brain swelling with or without bleeding and an increased risk for falls.[11]
Other medications including donepezil, rivastigmine, galantamine, and memantine may be prescribed to treat cognitive symptoms. However, they do not affect the underlying brain changes that cause Alzheimer’s disease and do not slow or stop the course of the disease. These medications work by affecting the levels of neurotransmitters in the brain.[12]
Brexpiprazole has been approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to treat agitation, a common symptom of Alzheimer’s disease. Brexpiprazole is an atypical antipsychotic drug that is associated with an increased risk of stroke and death in older patients with dementia-related psychosis, so nonpharmacological interventions should be attempted first.[13]
Interventions for Symptomatic Behavior
Many people find the behavioral changes caused by Alzheimer’s disease to be the most challenging and distressing effect of the disease. The chief cause of behavioral symptoms is the progressive deterioration of brain cells. However, medication, environmental influences, and some medical conditions can also cause symptoms or make them worse.
In the early stages of Alzheimer’s disease, people may experience behavior and personality changes, such as irritability, anxiety, and depression. In later stages, other symptoms may occur, including the following:
- Aggression and anger
- Anxiety and agitation
- General emotional distress
- Physical or verbal outbursts
- Restlessness, pacing, or shredding paper or tissues
- Hallucinations (seeing, hearing, or feeling things that are not really there)
- Delusions (firmly held beliefs in things that are not true)
- Sleep issues and sundowning
Sundowning is restlessness, agitation, irritability, or confusion that typically begins or worsens as daylight begins to fade and can continue into the night, making it hard for clients with Alzheimer’s to sleep. Being too tired can increase late-afternoon and early-evening restlessness. Tips to manage sundowning are as follows[14]:
- Take the person outside or expose them to bright light in the morning to reset their circadian rhythm.
- Do not plan too many activities during the day. A full schedule can be overtiring.
- Make early evening a quiet time of day. Play soothing music or ask a family member or friend to call during this time.
- Close the curtains or blinds at dusk to minimize shadows and the confusion they may cause.
- Reduce noise, clutter, or the number of people in the room.
- Do not serve coffee, cola, or other drinks with caffeine late in the day.
Aggressive Behaviors
Aggressive behaviors may be verbal or physical. They can occur suddenly, with no apparent reason, or result from a frustrating situation. While aggression can be hard to cope with, understanding this is a symptom of Alzheimer’s disease and the person with Alzheimer’s or dementia is not acting this way on purpose can help. See Figure 6.8[15] for an image of a resident with dementia demonstrating aggressive verbal behavior.

Aggression can be caused by many factors including physical discomfort, environmental factors, and poor communication. If the person with Alzheimer’s is aggressive, consider what might be contributing to the change in behavior.
Physical Discomfort
- Is the person able to let you know they are experiencing physical pain? It is not uncommon for persons with Alzheimer’s or other types of dementia to have chronic pain, urinary tract infections, or other conditions causing acute pain. Due to their loss of cognitive function, they are unable to articulate or identify the cause of physical discomfort and, therefore, may express it through physical aggression.
- Is the person tired because of inadequate rest or sleep?
- Is the person hungry or thirsty?
- Are medications causing side effects? Side effects are especially likely to occur when individuals are taking multiple medications for several health conditions.
Environmental Factors
- Is the person overstimulated by loud noises, an overactive environment, or physical clutter? Large crowds or being surrounded by unfamiliar people — even within one’s own home — can be overstimulating for a person with dementia.
- Does the person feel lost?
- What time of day is the person most alert? Most people function better during a certain time of day; typically, mornings are best. Consider the time of day when making appointments or scheduling activities. Choose a time when you know the person is most alert and best able to process new information or surroundings.
Poor Communication
- Are your instructions simple and easy to understand?
- Are you asking too many questions or making too many statements at once?
- Is the person picking up on your own stress or irritability?
Techniques for Response
There are many therapeutic methods for a nurse or caregiver to respond to aggressive behaviors displayed by a person with dementia. The following are some methods that can be used with aggressive behavior:
- Begin by trying to identify the immediate cause of the behavior. Think about what happened right before the reaction that may have triggered the behavior. Rule out pain as the cause of the behavior. Pain can trigger aggressive behavior for a person with dementia.
- Focus on the person’s feelings, not the facts. Look for the feelings behind the specific words or actions.
- Don’t get upset. Be positive and reassuring and speak slowly in a soft tone.
- Limit distractions. Examine the person’s surroundings, and adapt them to avoid future triggers.
- Implement a relaxing activity. Try music, massage, or exercise to help soothe the person.
- Shift the focus to another activity. The immediate situation or activity may have unintentionally caused the aggressive response, so try a different approach.
- Take a break if needed. If the person is in a safe environment and you are able, walk away and take a moment for emotions to cool.
- Ensure safety! Make sure you and the person are safe. Be aware of the location of the person’s hands and feet in the event they become combative and try to strike out, kick, or bite you. If these interventions do not successfully calm down the person, seek assistance from others. If it is an emergency situation, call 911 and be sure to tell the responders the person has dementia that causes them to act aggressively.
When educating caregivers about responding to aggressive behaviors, encourage them to share their experience with others, such as face-to-face support groups, where they can share response strategies they have tried and also get more ideas from other caregivers.
Anxiety and Agitation
A person with Alzheimer’s may feel anxious or agitated. They may become restless, causing a need to move around or pace or become upset in certain places or when focused on specific details. See Figure 6.9[16] for an illustration of an older adult feeling the need to move around. Anxiety and agitation can be caused by several medical conditions, medication interactions, or by any circumstances that worsen the person’s ability to think. Ultimately, the person with dementia is biologically experiencing a profound loss of their ability to negotiate new information and stimuli. It is a direct result of the disease. Situations that may lead to agitation can include moving to a new residence or nursing home; changes in environment, such as travel, hospitalization, or the presence of houseguests; changes in caregiver arrangements; misperceived threats; or fear and fatigue resulting from trying to make sense out of a confusing world.

Interventions to prevent and treat agitation include the following:
- Create a calm environment and remove stressors. This may involve moving the person to a safer or quieter place or offering a security object, rest, or privacy. Providing soothing rituals and limiting caffeine use are also helpful.
- Avoid environmental triggers. Noise, glare, and background distraction (such as having the television on) can act as triggers.
- Monitor personal comfort. Check for pain, hunger, thirst, constipation, full bladder, fatigue, infections, and skin irritation. Make sure the room is at a comfortable temperature. Be sensitive to the person’s fears, misperceived threats, and frustration with expressing what is wanted.
- Simplify tasks and routines.
- Find outlets for the person’s energy. The person may be looking for something to do. Provide an opportunity for exercise such as going for a walk or putting on music and dancing.
Techniques for Response
If a client with dementia becomes anxious or agitated, consider these potential interventions:
- Back off and ask permission before performing care tasks. Use calm, positive statements, slow down, add lighting, and provide reassurance. Offer guided choices between two options when possible. Focus on pleasant events and try to limit stimulation.
- Use effective language. When speaking, try phrases such as, “May I help you? Do you have time to help me? You’re safe here. Everything is under control. I apologize. I’m sorry that you are upset. I know it’s hard. I will stay with you until you feel better.”
- Listen to the person’s frustration. Find out what may be causing the agitation and try to understand.
- Check yourself. Do not raise your voice; show alarm or offense; or corner, crowd, restrain, criticize, ignore, or argue with the person. Take care not to make sudden movements out of the person’s view. Be aware of the client’s hands and feet in the event they strike out or kick at you.
If the person’s anxiety or agitation does not improve using these techniques, notify the provider to rule out physiological causes or medication-related side effects.
Hallucinations
When a person with dementia experiences hallucinations, they may see, hear, smell, taste, or feel something that isn’t there. Some hallucinations may be frightening, while others may involve ordinary visions of people, situations, or objects from the past. Alzheimer’s and other dementias are not the only cause of hallucinations. Other causes of hallucinations include schizophrenia; physical problems, such as kidney or bladder infections, dehydration, or intense pain; alcohol or drug abuse; eyesight or hearing problems; and medications. See Figure 6.10[17] for an illustration of hallucinations experienced by a person with dementia.

If a person with dementia begins hallucinating, notify the health care provider to rule out other possible causes and to determine if medication is needed. It may also help to have the person’s eyesight or hearing checked. If these strategies fail and symptoms are severe, medication may be prescribed. While antipsychotic medications can be effective in some situations, they are associated with an increased risk of stroke and death in older adults with dementia and must be used carefully.
Techniques for Response
When responding to a client with dementia experiencing hallucinations, be cautious. First, assess the situation and determine whether the hallucination is a problem for the person or for you. Is the hallucination upsetting? Is it leading the person to do something dangerous? Is the sight of an unfamiliar face causing the person to become frightened? If so, react calmly and quickly with reassuring words and a comforting touch. Do not argue with the person about what they see or hear. If the behavior is not dangerous, there may not be a need to intervene.
- Offer reassurance. Respond in a calm, supportive manner. You may want to respond with, “Don’t worry. I’m here. I’ll protect you. I’ll take care of you.” Gentle patting may turn the person’s attention toward you and reduce the hallucination.
- Acknowledge the feelings behind the hallucination and try to find out what the hallucination means to the individual. You might want to say, “It sounds as if you’re worried” or “This must be frightening for you.”
- Use distractions. Suggest a walk or move to another room. Frightening hallucinations often subside in well-lit areas where other people are present. Try to turn the person’s attention to music, conversation, or activities they enjoy.
- Respond honestly. If the person asks you about a hallucination or delusion, be honest. For example, if they ask, “Do you see the spider on the wall?,” you can respond, “I know you see something, but I don’t see it.” This way you’re not denying what the person sees or hears and avoiding escalating their agitation.
- Modify the environment. Check for sounds that might be misinterpreted, such as noise from a television or an air conditioner. Look for lighting that casts shadows, reflections, or distortions on the surfaces of floors, walls, and furniture. Turn on lights to reduce shadows. Cover mirrors with a cloth or remove them if the person thinks that he or she is looking at a stranger.
Sundowning
Sundowning is increased confusion, anxiety, agitation, pacing, and disorientation in clients with dementia that typically begins at dusk and continues throughout the night. Although the exact cause of sundowning and sleep disorders in people with Alzheimer’s disease is unknown, these changes result from the disease’s impact on the brain. There are several factors that may contribute to sleep disturbances and sundowning:
- Mental and physical exhaustion from a full day trying to keep up with an unfamiliar or confusing environment.
- An upset in the “internal body clock,” causing a biological mix-up between day and night.
- Reduced lighting causing shadows and misinterpretation is seen, causing agitation.
- Nonverbal behaviors of others, especially if stress or frustration is present.
- Disorientation due to the inability to separate dreams from reality when sleeping.
- Decreased need for sleep, a common condition among older adults.
There are several interventions that nurses and caregivers can implement to help manage sleep issues and sundowning:
- Promote plenty of rest.
- Encourage a regular routine of waking up, eating meals, and going to bed.
- When possible and appropriate, include walks or time outside in the sunlight.
- Make notes about what happens before sundowning events and try to identify triggers.
- Reduce stimulation during the evening hours (e.g., TV, doing chores, loud music, etc.). These distractions may add to the person’s confusion.
- Offer a larger meal at lunch and keep the evening meal lighter.
- Keep the home environment well-lit in the evening. Adequate lighting may reduce the person’s confusion.
- Do not physically restrain the person; it can make agitation worse.
- Try to identify activities that are soothing to the person, such as listening to calming music, looking at photographs, or watching a favorite movie.
- Take a walk with the person to help reduce their restlessness.
- Consider the best times of day for administering medication; consult with the prescribing provider or pharmacist as needed.
- Limit daytime naps if the person has trouble sleeping at night.
- Reduce or avoid alcohol, caffeine, and nicotine that can affect the ability to sleep.
- Discuss the situation with the provider when behavioral interventions and environmental changes do not work. Additional medications may be prescribed.
Caregiver Role Strain
Eighty-three percent of the help provided to people living with dementia in their homes in the United States comes from family members, friends, or other unpaid caregivers. Approximately one quarter of dementia caregivers are also “sandwich generation” caregivers — meaning that they care not only for an aging parent, but also for children under age 18. Dementia can take a devastating toll on caregivers. Compared with caregivers of people without dementia, twice as many caregivers of people with dementia indicate substantial emotional, financial, and physical difficulties.[18] See Figure 6.11[19] of an image of a caregiver daughter caring for her mother with dementia.

The caregivers of clients with dementia frequently report experiencing high levels of stress that often eventually impact their health and well-being. Nurses should monitor caregivers for these symptoms of stress:
- Denial about the disease and its effect on the person who has been diagnosed. For example, the caregiver might say, “I know Mom is going to get better.”
- Anger at the person with Alzheimer’s or frustration that they can’t do the things they used to be able to do. For example, the caregiver might say, “He knows how to get dressed — he’s just being stubborn.”
- Social withdrawal from friends and activities. For example, the caregiver may say, “I don’t care about visiting with my friends anymore.”
- Anxiety about the future and facing another day. For example, the caregiver might say, “What happens when he needs more care than I can provide?”
- Depression or decreased ability to cope. For example, the caregiver might say, “I just don’t care anymore.”
- Exhaustion that makes it difficult to complete necessary daily tasks. For example, the caregiver might say, “I’m too tired to prepare meals.”
- Sleeplessness caused by concerns. For example, the caregiver might say, “What if she wanders out of the house or falls and hurts herself?”
- Irritability, moodiness, or negative responses.
- Lack of concentration that makes it difficult to perform familiar tasks. For example, the caregiver might say, “I was so busy; I forgot my appointment.”
- Health problems that begin to take a mental and physical toll. For example, the caregiver might say, “I can’t remember the last time I felt good.”
Nurses should monitor for these signs of caregiver stress and provide information about community resources. (See additional information about community resources below.) Caregivers should be encouraged to take good care of themselves by visiting their health care provider, eating well, exercising, and getting plenty of rest. It is helpful to remind caregivers that “taking care of yourself and being healthy can help you be a better caregiver.” Teach them relaxation techniques, such as relaxation breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, visualization, and meditation.
Caregivers should also be educated about additional care options, such as adult day care, respite care, residential facilities, or hospice care. Adult day care centers offer people with dementia and other chronic illnesses the opportunity to be social and to participate in activities in a safe environment, while also giving their caregivers the opportunity to work, run errands, or take a break. Respite care can be provided at home (by a volunteer or paid service) or in a care setting, such as adult day care or residential facility, to provide the caregiver a much-needed break. If the person with Alzheimer’s or other dementia prefers a communal living environment or requires more care than can be safely provided at home, a residential facility may be the best option for providing care. Different types of facilities provide different levels of care, depending on the person’s needs. Hospice care is a type of care selected by clients who are terminally ill and whose health care provider has determined they are expected to live six months or less. It focuses on providing comfort and dignity at the end of life with supportive services that can be of great benefit to people in the final stages of dementia and their families.
Read about alternative care options and caregiver support at the Alzheimer Association web page.
Community Resources
Local Alzheimer’s Association chapters can connect families and caregivers with the resources they need to cope with the challenges of caring for individuals with Alzheimer’s. View examples of resources provided by the Alzheimer’s Association in the following box.
Find an Alzheimer’s Association chapter in your community by visiting the Find Your Local Chapter web page.
The Alzheimer’s Association 24/7 Helpline (800.272.3900) is available around the clock, 365 days a year. Through this free service, specialists and master’s-level clinicians offer confidential support and information to people living with dementia, caregivers, families, and the public.
The Alzheimer’s Association has a free virtual library web page devoted to resources that increase knowledge about Alzheimer’s and other dementias.[20]
- Alzheimer’s Association. (2025). What is Alzheimer's? Alzheimer’s Association. https://www.alz.org/alzheimers-dementia/what-is-alzheimers ↵
- National Institute on Aging. (2019). Alzheimer’s disease fact sheet. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. https://www.nia.nih.gov/health/alzheimers-disease-fact-sheet ↵
- Alzheimer’s Association. (2025). What is Alzheimer's? Alzheimer’s Association. https://www.alz.org/alzheimers-dementia/what-is-alzheimers ↵
- “Alzheimers_Disease.jpg” by BruceBlaus is licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0 and “24239522109_6b061a9d69_o.jpg” by NIH Image Gallery is licensed under CC0 ↵
- National Institute on Aging. (2017, August 23). How Alzheimer’s changes the brain [Video]. YouTube. All rights reserved. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hEw1Yq_4PaA ↵
- Alzheimer’s Association. (2025). What is Alzheimer's? Alzheimer’s Association. https://www.alz.org/alzheimers-dementia/what-is-alzheimers ↵
- Alzheimer’s Association. (2025). What is Alzheimer's? Alzheimer’s Association. https://www.alz.org/alzheimers-dementia/what-is-alzheimers ↵
- Ouldred, E., & Bryant, C. (2008). Dementia care. Part 1: Guidance and the assessment process. British Journal of Nursing, 17(3), 138-145. https://doi.org/10.12968/bjon.2008.17.3.28401 ↵
- “civilian-service-63616_960_720.jpg” by geralt is licensed under CC0 ↵
- Alzheimer’s Association. (2025). What is Alzheimer's? Alzheimer’s Association. https://www.alz.org/alzheimers-dementia/what-is-alzheimers ↵
- Alzheimer’s Association. (2025). What is Alzheimer's? Alzheimer’s Association. https://www.alz.org/alzheimers-dementia/what-is-alzheimers ↵
- Alzheimer’s Association. (2025). What is Alzheimer's? Alzheimer’s Association. https://www.alz.org/alzheimers-dementia/what-is-alzheimers ↵
- Alzheimer’s Association. (2025). What is Alzheimer's? Alzheimer’s Association. https://www.alz.org/alzheimers-dementia/what-is-alzheimers ↵
- National Institute on Aging. (n.d.). Tips for coping with sundowning. https://www.nia.nih.gov/health/tips-coping-sundowning ↵
- “5012292106_507e008c7a_o.jpg” by borosjuli is licensed under CC BY 2.0 ↵
- “old-63622_960_720.jpg” by geralt is licensed under CC0 ↵
- lewy-body-dementia-2965713_960_720.jpg” by Jetiveri is licensed under CC0 ↵
- Alzheimer’s Association. (2025). What is Alzheimer's? Alzheimer’s Association. https://www.alz.org/alzheimers-dementia/what-is-alzheimers ↵
- “My_mum_ill_with_dementia_with_me.png” by MariaMagdalens is licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0 ↵
- Alzheimer’s Association. (2025). What is Alzheimer's? Alzheimer’s Association. https://www.alz.org/alzheimers-dementia/what-is-alzheimers ↵
An irreversible, progressive brain disorder that slowly destroys memory and thinking skills and eventually the ability to carry out the simplest tasks.
Increased confusion, anxiety, agitation, pacing, and disorientation in patients with dementia that typically begins at dusk and continues throughout the night.
Care that offers people with dementia and other chronic illnesses the opportunity to be social and to participate in activities in a safe environment, while also giving their caregivers the opportunity to work, run errands, or take a much-needed break.
Care provided at home (by a volunteer or paid service) or in a care setting, such as adult day care or residential facility, that allows the caregiver to take a much-needed break.
A type of care selected by clients who are terminally ill and whose health care provider has determined they are expected to live six months or less that focuses on providing comfort and dignity at the end of life. It involves care and support services that can be of great benefit to people in the final stages of dementia and to their families.

