7.6 Measuring Weight and Height
Height and weight are documented upon admission to a facility as a baseline measurement and then taken routinely. Accurate weights are required for calculating medication dosages, ensuring adequate food and fluid intake, and monitoring chronic conditions such as heart failure (because weight gain is often the first indication of an impending problem).
If a resident requires daily weights as documented in their care plan, their weight should be taken on the same scale at the same time every day, before any food or fluids are consumed, and while wearing a similar amount of clothing. The weight is documented, and weight changes of 3 pounds over 24 hours or 5 pounds within a week should be immediately reported to the nurse to address any possible complications. See the “Measuring Weight for Ambulatory Residents” Skills Checklist for measuring weight for more details.
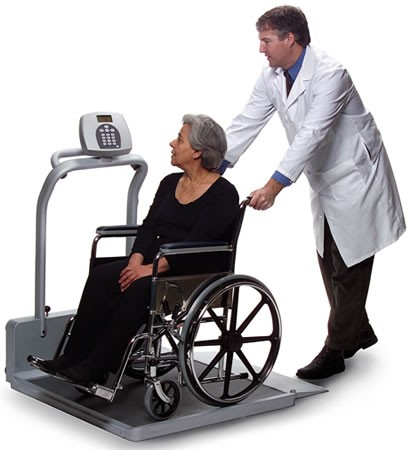
If a resident is nonambulatory, the nursing assistant should weigh the wheelchair and any associated accessories (such as foot pedals or a chair cushion). After the resident is dressed and groomed, the nursing assistant should bring them to the scale, obtain the weight, and then subtract the weight of the chair and associated accessories. See Figure 7.13[1] for an image of weighing a resident on a wheelchair scale.
If a resident requires transfer with a full-body mechanical lift, some lifts have a scale function that can weigh the resident as they transfer from bed to wheelchair.
Height
Resident height is typically obtained on admission and documented in the medical record. Because height rarely changes, measurement is rarely repeated. See the “Measuring Height for Ambulatory Residents” Skills Checklist for measuring the height of an ambulatory person with a stadiometer. Figure 7.14[2] shows a person being measured with a stadiometer. If a resident is nonambulatory or unable to stand, their height can be measured with a tape measure while they are lying in bed. Height is recorded in inches or millimeters based on agency policy.

Body Mass Index
Nursing assistants may be asked to obtain a height and weight to calculate a resident’s Body Mass Index (BMI). Body mass index (BMI) is a calculated measure of body fat based on a person’s height and weight. It is calculated by dividing weight in kilograms by the square of their height in meters. BMI is used to evaluate if an individual is underweight (BMI less than 18.5), normal (BMI 18.6-24.9), overweight (BMI over 25), or obese (BMI over 30). Elevated BMI measurements are associated with cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, and other chronic diseases.[3]
- “HOM-2600KL-2.jpg by unknown author is used on the basis of Fair Use. ↵
- “stadiometer-3.jpeg” by unknown author is used on the basis of Fair Use. ↵
- This work is a derivative of StatPearls by McNeil-Masuka and Boyer and is licensed under CC BY 4.0 ↵
Client weight taken at the same time every day, on the same scale, in similar clothing, and before any food or fluids are consumed.
A calculated measure of body fat based on a person’s height and weight.

