8.5 Assisting With Ambulation
Ambulation is the medical term used for walking. Ambulation provides weight-bearing activity that promotes bone health and joint mobility. A physical therapist will determine if a person can safely walk independently, with the assistance of one or two people, or if they require an assistive device such as a cane or walker. This information is documented in their nursing care plan. Similar to when assisting a client to transfer with a gait belt, the nursing assistant should place nonskid footwear on the person and allow them to dangle on the edge of the bed before standing to ambulate. For specific steps, see the “Ambulation From Wheelchair” Skills Checklist.
If a resident requires assistance with a cane, the cane should be placed on the resident’s stronger side. The resident should step forward with the strong leg and then use the cane and the weaker leg for the next step.
There are three types of walkers: a standard walker, a two-wheeled walker (2WW), and a four-wheeled walker (4WW). The type of walker a resident should use is recommended by the physical therapist. A 2WW or standard walker allows for more support and a slower gait, whereas a 4WW is used by clients with better balance and mobility.
View a YouTube video[1] of an instructor demonstrating helping clients with ambulatory assistive devices:
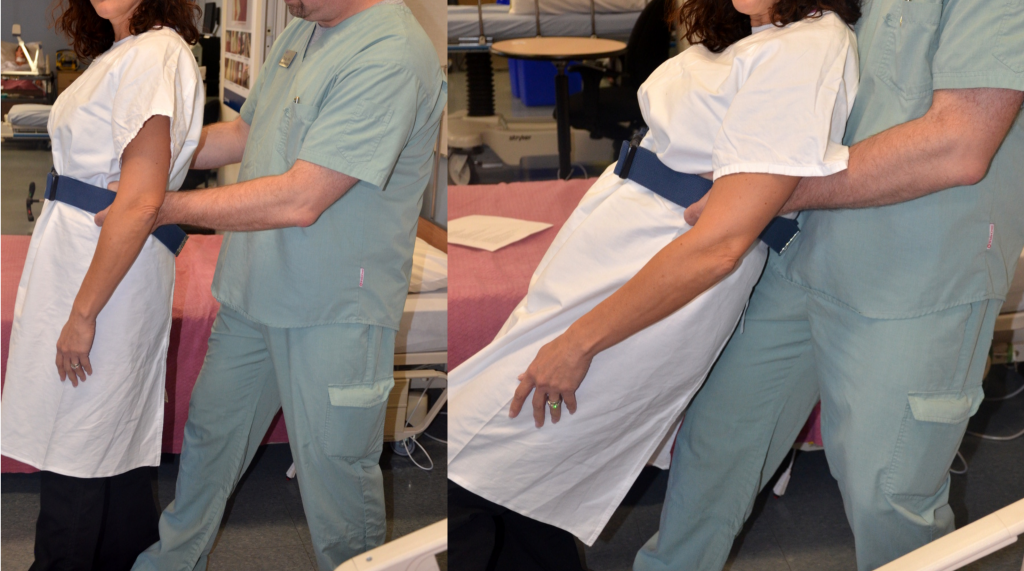
Regardless of the assistive device used for ambulation, the NA should remind the resident to stand up straight and look forward when walking. The resident should be encouraged to take purposeful steps and to not shuffle their feet. The NA should stand to one side of the resident and slightly behind them, with one hand on their gait belt. If the resident has a weaker side, the NA should stand on that side. The NA’s fingertips should be facing upwards underneath the gait belt for proper support. If the resident loses their balance while in this position, the NA’s arm will allow them to use their bicep muscle, rather than their forearm, to steady the client. The bicep is larger and stronger than the forearm and can provide better support.
A second staff member can follow a resident who is ambulating with assistance with their wheelchair in case they experience weakness or dizziness. If the client needs to sit while ambulating, the wheelchair brakes should be applied before they sit, or in an emergent situation, the NA should block the back of the wheelchair with their body to ensure stability when the resident sits.
If a resident starts to fall while standing or ambulating, do not attempt to stop their fall or catch the resident because this can cause you to injure your back. Instead, move behind the patient and take one step back with one leg so you have a wide base of support. Support the patient around their waist or hip area or grab the gait belt. Bend one of your legs and place it between the patient’s legs from behind. Slowly slide the patient down your bent leg, lowering yourself to the floor at the same time. Always protect the resident’s head to prevent head injury. After the resident is on the floor, do not move them. For witnessed or unwitnessed falls, notify the nurse immediately for assessment. After the nurse has completed the assessment and met the resident’s immediate needs, use a mechanical lift to transfer the resident back to a wheelchair or bed. An incident report will be completed by the nurse, and the NA will be asked to give a statement on what occurred and their actions in response to the situation.[2] See Figure 8.21[3] for an image of lowering a resident who is falling to the floor.
- Chippewa Valley Technical College. (2022, December 3). Ambulatory Assistive Devices. [Video]. YouTube. Video licensed under CC BY 4.0. https://youtu.be/ATn7OOP4Jko ↵
- This work is a derivative of Nursing Fundamentals by Chippewa Valley Technical College and is licensed under CC BY 4.0 ↵
- “Sept-22-2015-132-001.jpg” and “Sept-22-2015-133.jpg” by unknown authors are licensed under CC BY 4.0. Access for free at https://opentextbc.ca/clinicalskills/chapter/3-7-fall-prevention/ ↵
The medical term used for walking.

