3.12 Aminoglycosides
Aminoglycosides are potent broad-spectrum antibiotics that are useful for treating severe infections. Many aminoglycosides are poorly absorbed in the GI tract; therefore, the majority are given IV or IM. Aminoglycosides are potentially nephrotoxic and neurotoxic and should be administered cautiously. Blood peak and trough levels should be performed to titrate a safe dose for each client.
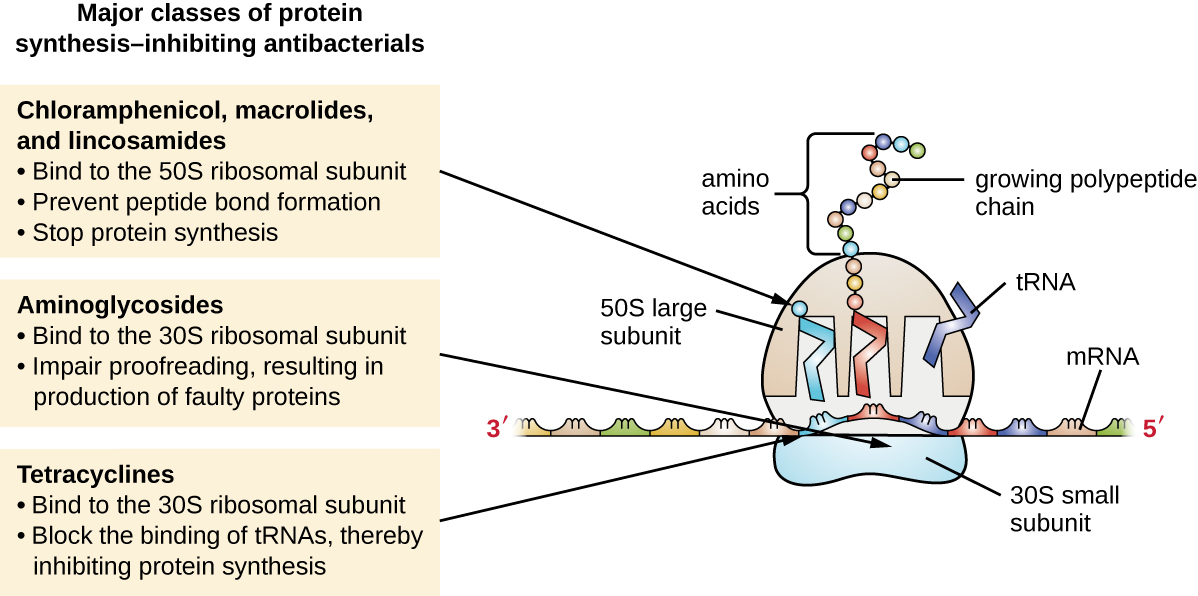
Mechanism of Action: Aminoglycosides are bactericidal and bind with the area of the ribosome known as the 30S subunit, inhibiting protein synthesis in the cell wall and resulting in bacterial death (see Figure 3.7).[1] Aminoglycosides may be given with beta-lactam medications to facilitate transport of aminoglycoside across the cellular membrane, resulting in a synergistic effect and increasing drug effectiveness.
Indications: Streptomycin is used for streptococcal endocarditis and a second-line treatment for tuberculosis. Gentamicin is used to treat serious gram-negative infections caused by bacteria such as meningitis (infection of the membranes that surround the brain and spinal cord) and serious infections of the blood, abdomen, lungs, skin, bones, joints, and urinary tract based on culture results.
Nursing Considerations: Aminoglycosides can result in many adverse effects for the client and, therefore, the nurse should monitor the client carefully for signs of emerging concerns. Peak and trough levels are used to titrate this medication to a safe dose. Aminoglycosides can be nephrotoxic (damaging to kidney), neurotoxic (damaging to the nervous system), and ototoxic (damaging to the ear). Nurses should monitor the client receiving aminoglycosides for signs of decreased renal function such as declining urine output and increasing blood urea nitrogen (BUN), increasing creatinine, and declining glomerular filtration rate (GFR). Indications of damage to the neurological system may be assessed as increasing peripheral numbness or tingling in the extremities. Additionally, the client should be carefully assessed for hearing loss or hearing changes throughout the course of drug administration.
Side Effects/Adverse Effects: Common side effects of aminoglycosides include GI upset and rash. New onset of diarrhea can indicate C-diff and should be reported immediately to the provider. Renal function must be closely monitored to watch for onset of nephrotoxicity. Clients have an increased risk for severe neurotoxic reactions, especially with renal impairment. Additionally, the administration of aminoglycosides can result in respiratory paralysis if given soon after anesthesia or a muscle relaxant. There is also increased risk for ototoxicity when administered with a loop diuretic. The administration of aminoglycosides can cause harm to a fetus and breastfed infants.
Health Teaching & Health Promotion: Clients receiving aminoglycosides should be advised to monitor for signs of hypersensitivity and auditory changes. This may include tinnitus and hearing loss. Clients may also experience accompanying vertigo while on the medication. Clients should be advised to drink plenty of fluids while taking the medication to reduce the risk of nephrotoxicity. Female clients should notify their provider if pregnancy is planned or if they are actively breastfeeding.[2]
Now let’s take a closer look at the medication grid for streptomycin and gentamycin in Table 3.12.[3]
Table 3.12 Streptomycin and Gentamycin Medication Grid
Class/Subclass |
Prototype/Generic |
Nursing Considerations |
Therapeutic Effects |
Side/Adverse Effects |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aminoglycosides | streptomycin | Check for allergies
Obtain culture before administering Blood sample for peak level should be obtained after administration; obtain blood sample for trough level just before administering next dose Inject into a large muscle Handle carefully; use gloves to prepare Monitor peak and trough levels |
Monitor for systemic signs of infection:
-WBCs -Fever Monitor actual site of infection Monitor culture results |
GI upset
Rash Report signs of C-diff (diarrhea) immediately SAFETY: Risk for severe neurotoxic reactions, especially with renal impairment. Can result in respiratory paralysis if given soon after anesthesia or muscle relaxant Risk for ototoxicity, especially if administered with a loop diuretic Can cause harm to fetus and breastfed infants |
Critical Thinking Activity 3.12
Using the above grid information, consider the following clinical scenario question:
A client is admitted with streptococcal endocarditis, and the nurse is preparing the morning dose of streptomycin. The lab has not yet arrived to obtain the trough level, and the drug is now overdue to be given. What is the nurse’s next best response?
Note: Answers to the Critical Thinking activities can be found in the “Answer Key” section at the end of the book.
- This work is a derivative of Microbiology by OpenStax licensed under CC BY 4.0. Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/microbiology/pages/1-introduction ↵
- uCentral from Unbound Medicine. https://www.unboundmedicine.com/ucentral ↵
- This work is a derivative of DailyMed by U.S. National Library of Medicine in the Public Domain. ↵

