1.2 Pharmacokinetics
Pharmacokinetics – Examining the Interaction of Body and Drug
Overview
Pharmacokinetics is the term that describes the four stages of absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion of drugs. Drugs are medications or other substances that have a physiological effect when introduced to the body. There are four basic stages a medication goes through within the human body: absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion. This entire process is sometimes abbreviated ADME.
Absorption is the first stage of pharmacokinetics and occurs after medications enter the body and travel from the site of administration into the body’s circulation. Distribution is the second stage of pharmacokinetics. It is the process by which medication is spread throughout the body. Metabolism is the third stage of pharmacokinetics and involves the breakdown of a drug molecule. Excretion is the final stage of pharmacokinetics and refers to the process in which the body eliminates waste. Each of these stages is described separately in the following sections of this chapter.
Research scientists who specialize in pharmacokinetics must also pay attention to another dimension of drug action within the body: time. Scientists do not have the ability to visualize where a drug is going or how long it is active. To compensate, they use mathematical models and precise measurements of blood and urine to determine where a drug goes and how much of the drug (or breakdown product) remains after the body processes it. Other indicators, such as blood levels of liver enzymes, can help predict how much of a drug is going to be absorbed.
Principles of chemistry are also applied while studying pharmacokinetics because the interactions between drugs and body molecules represent a series of chemical reactions. Understanding the chemical encounters between drugs and biological environments, such as the bloodstream and the oily surfaces of cells, is necessary to predict how much of a drug will be metabolized by the body.
Pharmacodynamics refers to the effects of drugs in the body and the mechanism of their action. As a drug travels through the bloodstream, it exhibits a unique affinity for a drug-receptor site, meaning how strongly it binds to the site. Drugs and receptor sites create a lock and key system (see Figure 1.1[1]) that affect how drugs work and the presence of a drug in the bloodstream after it is administered. This concept is broadly termed as drug bioavailability.
The bioavailability of drugs is an important feature that chemists and pharmaceutical scientists keep in mind when designing and packaging medicines. However, no matter how effectively a drug works in a laboratory simulation, the performance in the human body will not always produce the same results, and individualized responses to drugs have to be considered. Although many responses to medications may be anticipated, a person’s unique genetic makeup may significantly impact their response to a drug. Pharmacogenetics is defined as the study of how people’s genes affect their response to medicines.[2]
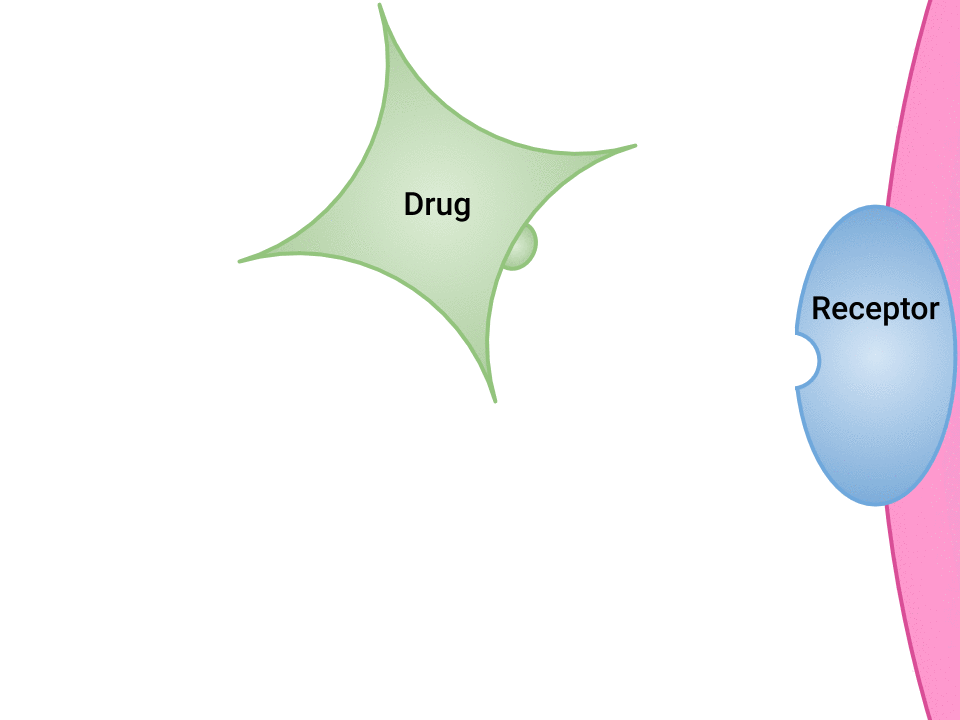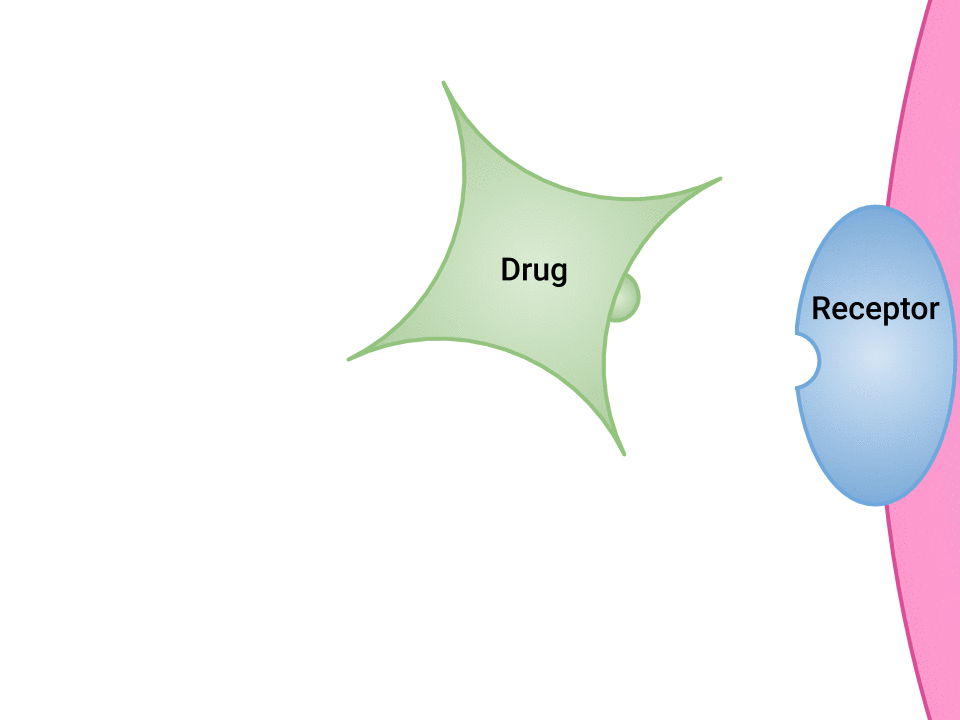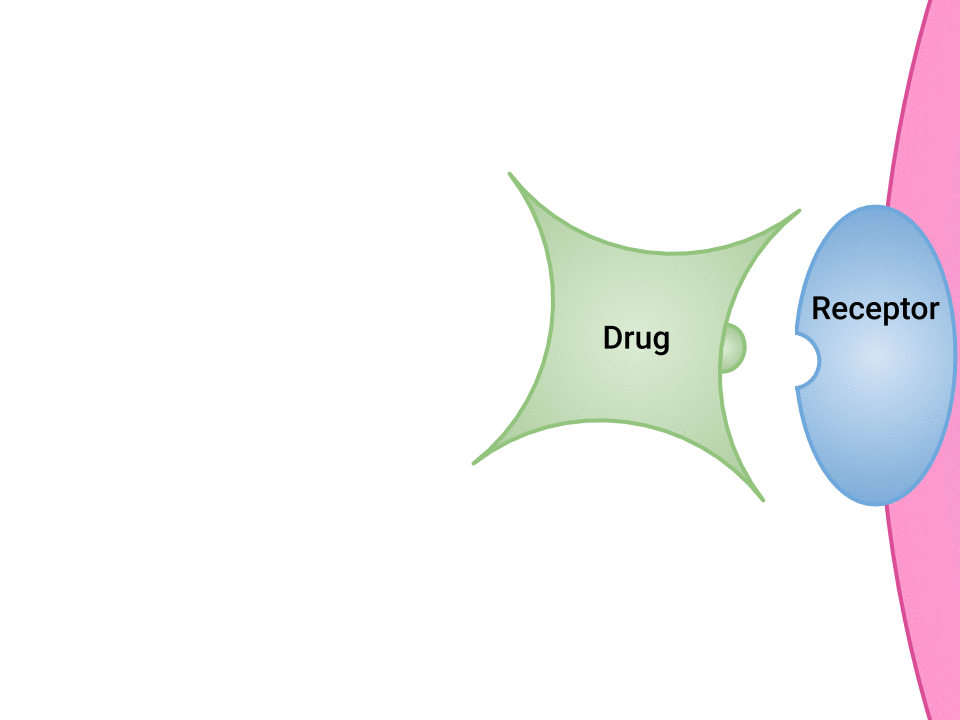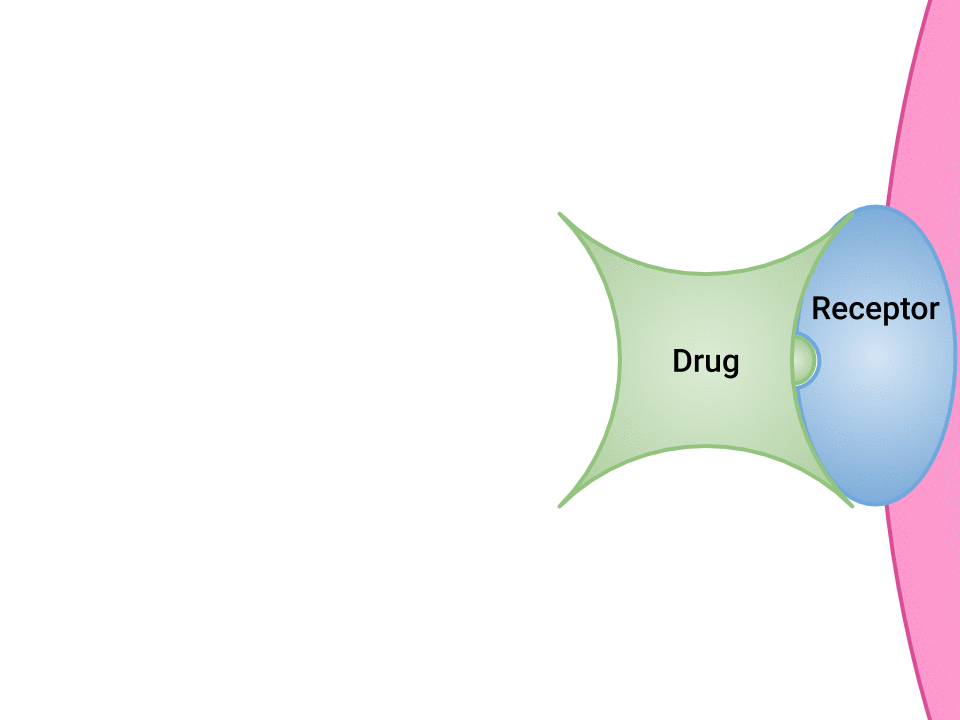
- “Drug and Receptor Binding” by Dominic Slausen at Chippewa Valley Technical College is licensed under CC BY 4.0 ↵
- This work is a derivative of Medicines by Design by US Department of Health and Human Services, National Institutes of Health, National Institute of General Medical Sciences and is available in the Public Domain. ↵
Describes the stages of absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion of drugs.
Medications or other substances that have a physiological effect when introduced to the body.
Acronym that describes the four basic stages for a medication to go through within the human body: Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, and Excretion.
After medications enter the body and travel from the site of administration into the body's circulation.
The second stage of pharmacokinetics; the process by which medication is dispersed throughout the body.
The breakdown of a drug molecule.
The final stage of pharmacokinetics; process by which the body eliminates waste or excess.
The study of how drugs act at target sites of action in the body.
The strength of binding between drug and receptor.
The ability of a drug or other chemical to be taken up by the body and made available in the tissue where it is needed.
The study of how people's genes affect their response to medicines.

