4.1 Introduction
Learning Objectives
- Outline indications for insertion of a central venous access device (CVAD)
- Compare and contrast the various types of CVADs and where they are inserted
- Describe the processes of verifying placement and securing a CVAD
- Describe infection control techniques to prevent infections associated with CVADs
- Identify potential complications associated with CVADs, prevention, and related nursing interventions
- Discuss how to safely change CVAD dressings and needleless connectors
- Outline the processes of safely accessing, flushing, and locking CVADs
- Describe blood sampling techniques from CVADs
- Discuss the components of routine documentation related to CVADs
As the complexity of client conditions continues to evolve within health care settings, the safe use and management of central lines are imperative. A central line is a thin, flexible, large-bore tube inserted into a client’s large vein, also referred to as a central venous access device (CVAD). There are various insertion sites for CVADs (see Figure 4.1[1]). CVADs are commonly guided into the superior vena cava so the distal tip is located in the superior vena cava near the junction with the right atrium. Other CVADs are introduced through the femoral vein so the distal tip sits in the inferior vena cava. CVADs differ from short peripheral IV catheters used for intravenous access because they are placed in central circulation due to the distal tip location.
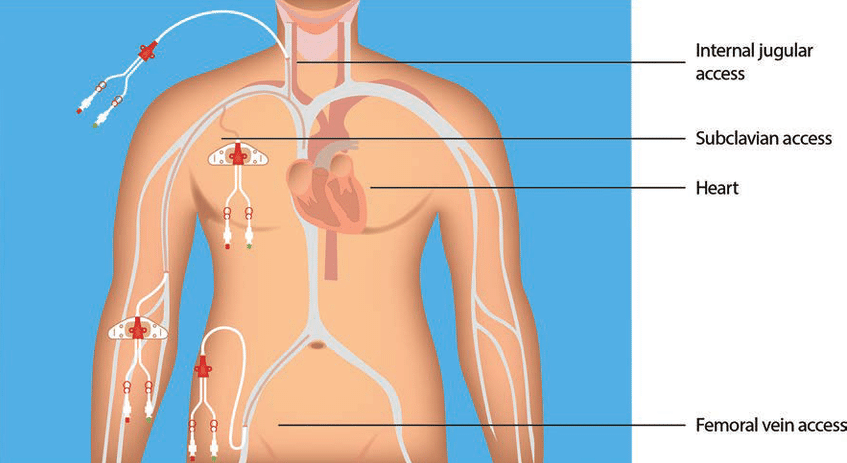
CVADs are used for delivery of medication, fluids, and nutrition and most can remain in place long-term. They can also be used for blood draws, hemodynamic monitoring, and transvenous pacing. These lines help ensure consistent vascular access can be easily obtained and utilized by the health care team. This chapter will describe indications for CVADs, explore different types of CVADs, outline related nursing procedures, and discuss nursing management of clients with CVADs.
- “Central-venous-access-sites.png” by unknown author is licensed under CC B-NC-ND. Access for free at https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Central-venous-access-sites_fig1_334584348 ↵
A thin, flexible, large-bore tube inserted into a client’s large vein.

