7.2 Feminism and Sexism
Learning Objectives
- Define feminism, sexism, and patriarchy.
- Discuss evidence for a decline in sexism.
In the national General Social Survey (GSS), slightly more than one-third of the public agrees with this statement: “It is much better for everyone involved if the man is the achiever outside the home and the woman takes care of the home and family.” Do you agree or disagree with this statement? If you are like the majority of college students, you disagree.
Today a lot of women, and some men, will say, “I’m not a feminist, but…,” and then go on to add that they hold certain beliefs about women’s equality and traditional gender roles that actually fall into a feminist framework. Their reluctance to self-identify as feminists underscores the negative image that feminists and feminism have but also suggests that the actual meaning of feminism may be unclear.
Feminism and sexism are generally two sides of the same coin. Feminism refers to the belief that women and men should have equal opportunities in economic, political, and social life, while sexism refers to a belief in traditional gender role stereotypes and in the inherent inequality between men and women. Sexism thus parallels the concept of racial and ethnic prejudice discussed in Chapter 6 “Racial and Ethnic Inequality”. Women and people of color are both said, for biological and/or cultural reasons, to lack certain qualities for success in today’s world.

The US Library of Congress – public domain; The US Library of Congress – public domain.
Two feminist movements in US history have greatly advanced the cause of women’s equality and changed views about gender. The first began during the abolitionist period, when abolitionists such as Susan B. Anthony, Lucretia Mott, and Elizabeth Cady Stanton began to see similarities between slavery and the oppression of women. This new women’s movement focused on many issues but especially the right to vote, which women won in 1920. The second major feminist movement began in the late 1960s, as women active in the Southern civil rights movement turned their attention to women’s rights, and it is still active today. This movement has profoundly changed public thinking and social and economic institutions, but, as we will soon see, much gender inequality remains.
Several varieties of feminism exist. Although they all share the basic idea that women and men should be equal in their opportunities in all spheres of life, they differ in other ways (Hannam, 2012). Liberal feminism believes that the equality of women can be achieved within our existing society by passing laws and reforming social, economic, and political institutions. In contrast, socialist feminism blames capitalism for women’s inequality and says that true gender equality can result only if fundamental changes in social institutions, and even a socialist revolution, are achieved. Radical feminism, on the other hand, says that patriarchy (male domination) lies at the root of women’s oppression and that women are oppressed even in noncapitalist societies. Patriarchy itself must be abolished, they say, if women are to become equal to men. Finally, multicultural feminism emphasizes that women of color are oppressed not only because of their gender but also because of their race and class. They thus face a triple burden that goes beyond their gender. By focusing their attention on women of color in the United States and other nations, multicultural feminists remind us that the lives of these women differ in many ways from those of the middle-class women who historically have led US feminist movements.
The Growth of Feminism and the Decline of Sexism
What evidence is there for the impact of the contemporary women’s movement on public thinking? The GSS, the Gallup poll, and other national surveys show that the public has moved away from traditional views of gender toward more modern ones. Another way of saying this is that the public has moved from sexism toward feminism.
To illustrate this, let’s return to the GSS statement that it is much better for the man to achieve outside the home and for the woman to take care of home and family. Figure 4.2 “Change in Acceptance of Traditional Gender Roles in the Family, 1977–2010” shows that agreement with this statement dropped sharply during the 1970s and 1980s before leveling off afterward to slightly more than one-third of the public.
Figure 4.2 Change in Acceptance of Traditional Gender Roles in the Family, 1977–2010
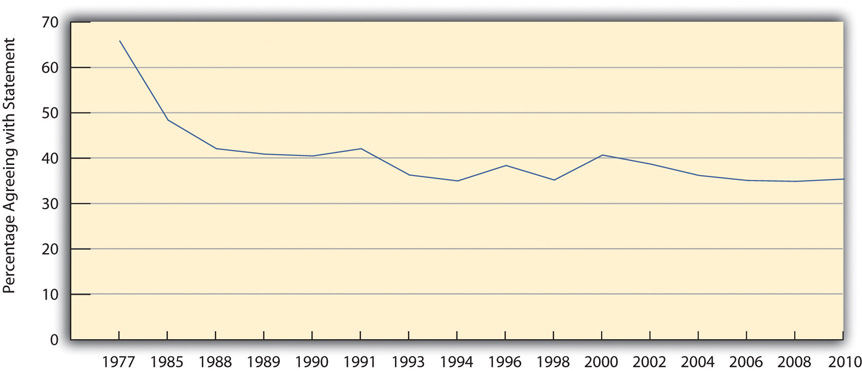
Source: Data from General Social Surveys. (1977–2010). Retrieved from http://sda.berkeley.edu/cgi-bin/hsda?harcsda+gss10.
Another GSS question over the years has asked whether respondents would be willing to vote for a qualified woman for president of the United States. As Figure 4.3 “Change in Willingness to Vote for a Qualified Woman for President” illustrates, this percentage rose from 74 percent in the early 1970s to a high of 96.2 percent in 2010. Although we have not yet had a woman president, despite Hillary Rodham Clinton’s historic presidential primary campaign in 2007 and 2008 and Sarah Palin’s presence on the Republican ticket in 2008, the survey evidence indicates the public is willing to vote for one. As demonstrated by the responses to the survey questions on women’s home roles and on a woman president, traditional gender views have indeed declined.
Figure 4.3 Change in Willingness to Vote for a Qualified Woman for President
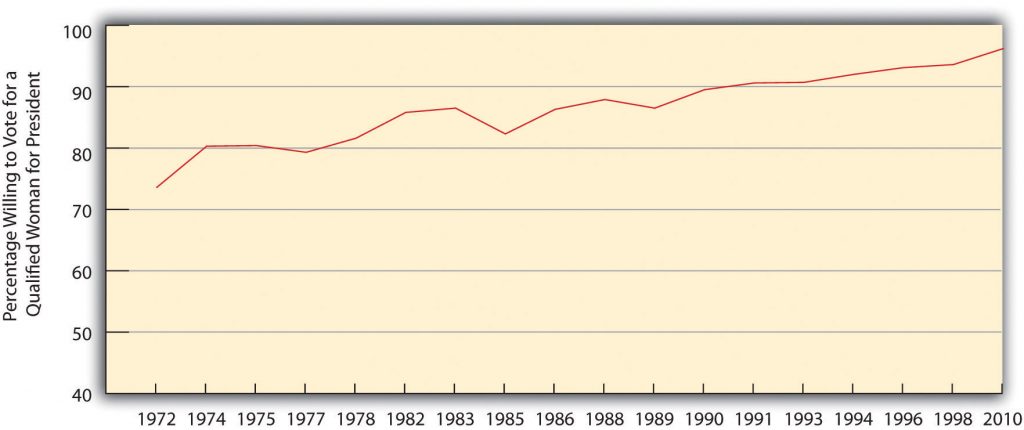
Source: Data from General Social Survey. (2010). Retrieved from http://sda.berkeley.edu/cgi-bin/hsda?harcsda+gss10.
Key Takeaways
- Feminism refers to the belief that women and men should have equal opportunities in economic, political, and social life, while sexism refers to a belief in traditional gender role stereotypes and in the inherent inequality between men and women.
- Sexist beliefs have declined in the United States since the early 1970s.
For Your Review
- Do you consider yourself a feminist? Why or why not?
- Think about one of your parents or of another adult much older than you. Does this person hold more traditional views about gender than you do? Explain your answer.
References
Hannam, J. (2012). Feminism. New York, NY: Pearson Longman.
Social Problems : Continuity and Change is adapted from a work produced and distributed under a Creative Commons license (CC BY-NC-SA) in 2010 by a publisher who has requested that they and the original author not receive attribution.
This adapted chapter is produced by Northeast Wisconsin Technical College. This adaptation has not significantly altered or updated the original 2010 text other than renumbering. This work is made available under the terms of a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike license.

