6.2 Major Functions of the Skeletal System
Major Functions of the Skeletal System[1]
The skeletal system performs five important functions for the human body, including support, protection, movement, storage, and blood cell production.
Support
Just as the steel beams of a building provide a scaffold to support its weight, the bones, ligaments, and cartilage of the skeletal system form a framework to support the weight of the body. Bones also give shape to the body, such as the face. Without the skeletal system, the body would just be a limp blob of organs, muscle, and skin.
Protection
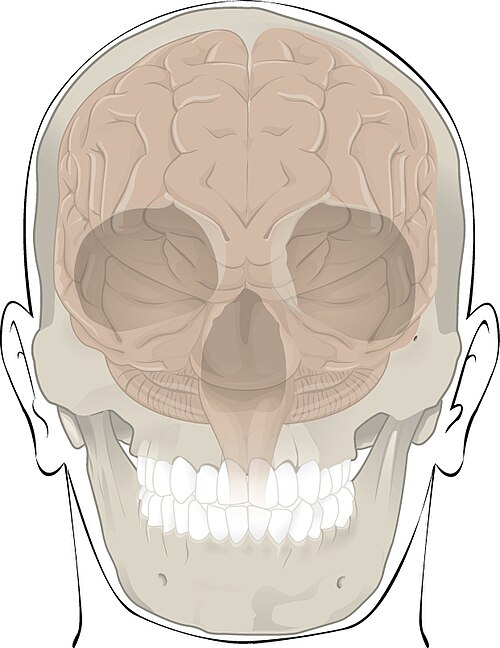
Bones protect internal organs from injury by covering or surrounding them. For example, the ribs protect the lungs and heart, bones of the vertebral column (spine) protect the spinal cord, and the cranium (skull) protects the brain. See Figure 6.2[2] for an illustration of how the cranium completely surrounds and protects the brain from injury.
Movement
Bones facilitate movement by serving as attachment points for muscles. Some bones only serve as a support for the muscles; others also transmit the forces produced when your muscles contract. From a mechanical point of view, bones act as levers and joints serve as fulcrums. See Figure 6.3[3] for an image depicting how bones facilitate movement.
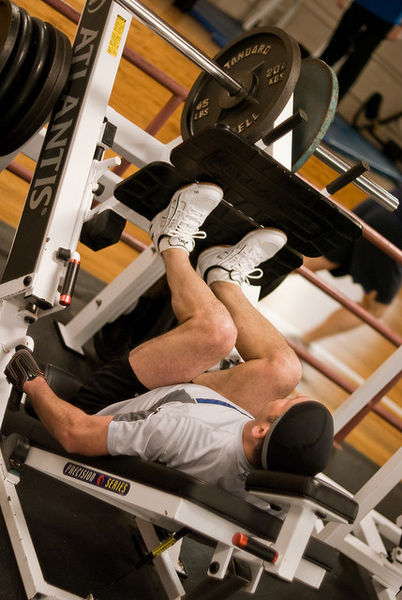

Storage
Bone stores a number of important minerals such as calcium and phosphorus. These minerals can be stored or released back into the bloodstream to maintain normal levels.
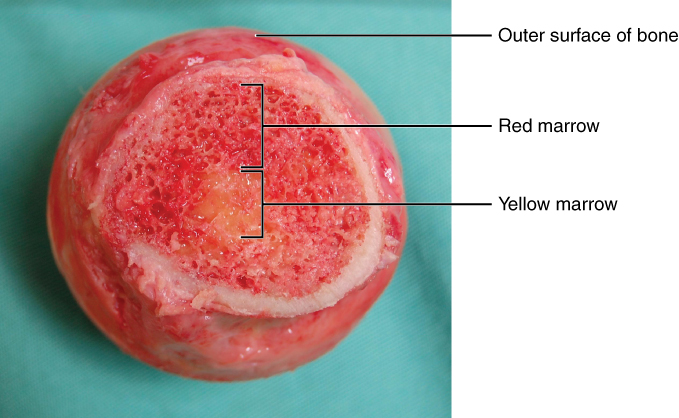
Bone also serves as a site for fat storage. The softer connective tissue that fills the inside of most bone is referred to as bone marrow. There are two types of bone marrow called yellow marrow and red marrow. Yellow bone marrow contains adipose tissue and stores triglycerides that can be used for energy. Red bone marrow produces blood cells, as described in the following subsection. See Figure 6.4[4] for an image of red and yellow bone marrow.
Blood Cell Production
Bone is also a site for blood cell production. Red bone marrow is where hemopoiesis (the production of blood cells) takes place. Red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets are all produced in the red bone marrow.
- Ernstmeyer, K., & Christman, E. (Eds.). (2024). Medical terminology 2e. Open RN | WisTech Open. https://wtcs.pressbooks.pub/medterm/ ↵
- “618_Bones_Protect_Brain.jpg” by OpenStax College is licensed under CC BY 3.0 ↵
- “Leg_press” by bozdoz is licensed under CC BY 2.0 ↵
- “619_Red_and_Yellow_Bone_Marrow” by OpenStax College is licensed under CC BY 3.0 ↵
A type of bone marrow which contains adipose tissue and stores triglycerides that can be used for energy.
A type of bone marrow that produces blood cells.
The production of blood cells.

