1.4 Anatomical Position
Anatomical Position[1],[2]
Health care professionals use precise medical terminology when communicating detailed information about the body and its anatomy to reduce medical errors that can result from ambiguity. To further increase precision, a standardized anatomical view of the body is used. Just like paper maps are oriented with north at the top of the page, the standard anatomical position is agreed on by the international medical community. In this position, a person is standing upright with the legs together or slightly apart, feet flat on the floor and facing forward, arms at the sides with the palms facing forward and thumbs pointing away from the body, and head and eyes straight ahead. In addition, the arms are usually placed slightly apart from the body so that the hands do not touch the sides. See Figure 1.4[3] for an illustration of the standard anatomical position.
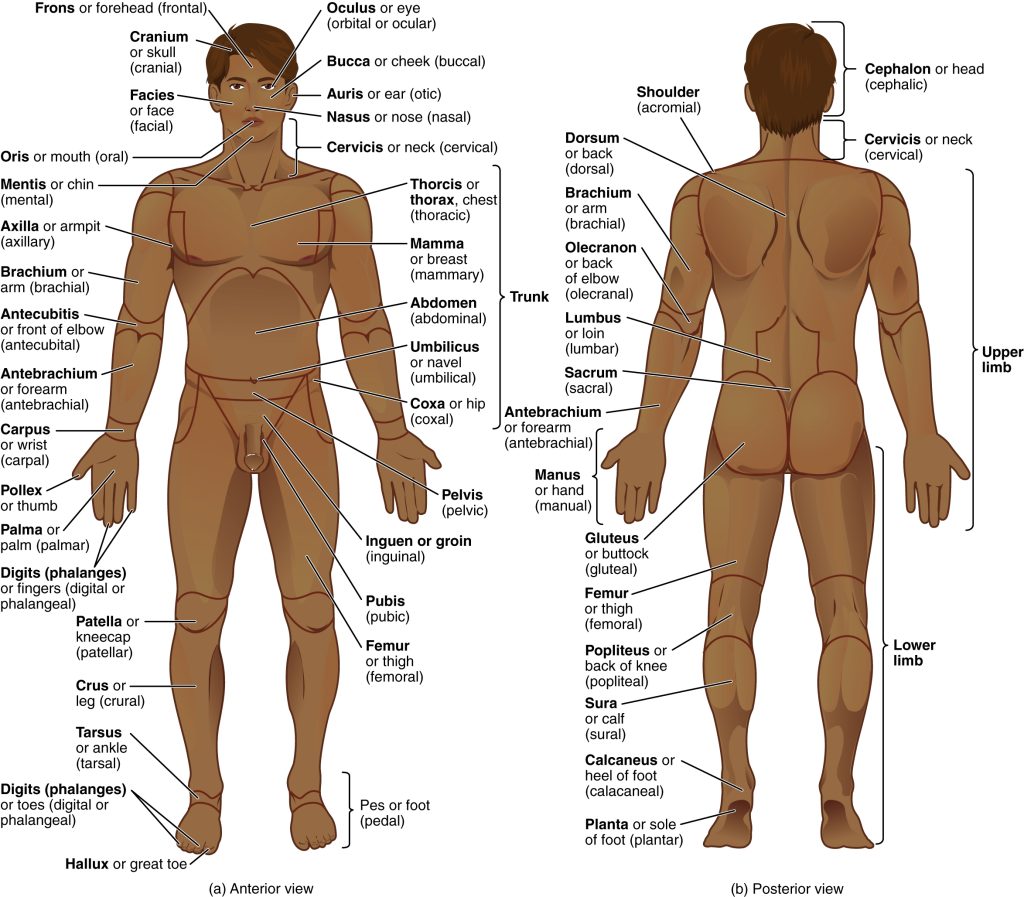
Regional terms are used to identify specific regions or areas of the body. For example, as illustrated in Figure 1.4, brachial refers to the “upper arm,” and antebrachial refers to the “lower arm” or “forearm.” Similarly, femoral refers to the “upper leg” and popliteal refers to the area behind the knee.
View a supplementary YouTube video[4] on standard anatomical position: The Anatomical Position | Body Planes & Directional Terms | Animated Music Video.
Prone and Supine
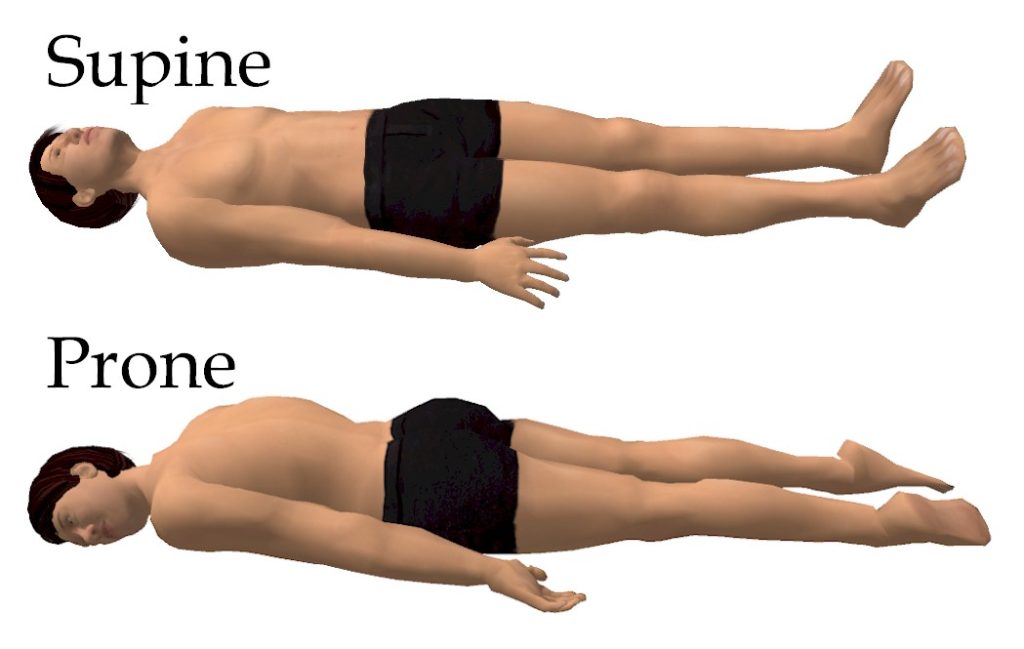
A body that is lying down is described as either prone or supine. These terms are often used to describe the position of the body during examinations or surgical procedures.
See Figure 1.5[5] for an illustration of prone and supine positions.
- Betts, J. G., Young, K. A., Wise, J. A., Johnson, E., Poe, B., Kruse, D. H., Korol, O., Johnson, J. E., Womble, M., & DeSaix, P. (2022). Anatomy and physiology 2e. OpenStax. https://openstax.org/books/anatomy-and-physiology-2e/pages/1-introduction ↵
- Boundless. (n.d.). Boundless anatomy and physiology. Lumen Learning. https://university.pressbooks.pub/test456/ ↵
- “f809b006c4ba0de05e1fe5462ef7236e28c7186f” by OpenStax is licensed under CC BY 4.0. Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/anatomy-and-physiology/pages/1-1-overview-of-anatomy-and-physiology ↵
- Biology Music Videos. (2021, May 12). The anatomical position | Body planes & directional terms | Animated music video [Video]. YouTube. All rights reserved. https://youtu.be/o35dd6Imgg8?feature=shared ↵
- “Supine_and_prone_2012-02-20” by Asanagi is licensed under CC0, Public Domain ↵
Positioning agreed upon by the international medical community in which a person is standing upright with the legs together or slightly apart, feet flat on the floor and facing forward, arms at the sides with the palms facing forward and thumbs pointing away from the body, and head and eyes straight ahead.
The body lying face-down.
The body lying face-up.

