5.2 Major Functions of the Integumentary System
Major Functions of the Integumentary System[1]
The skin and accessory structures have four main functions:
- Protection: The skin protects the body from outside elements (wind, rain, and ultraviolet radiation exposure); dehydration (excessive water loss); and entry of dirt, microbes, or harmful chemicals into the body.
- Sensation: The epidermis, dermis, and the hypodermis contain sensory nerve structures that detect touch, temperature, vibration, pressure, and pain. These receptors are more concentrated on the tips of the fingers, making them most sensitive to touch. Sensory receptors help us interpret our environment and react accordingly.
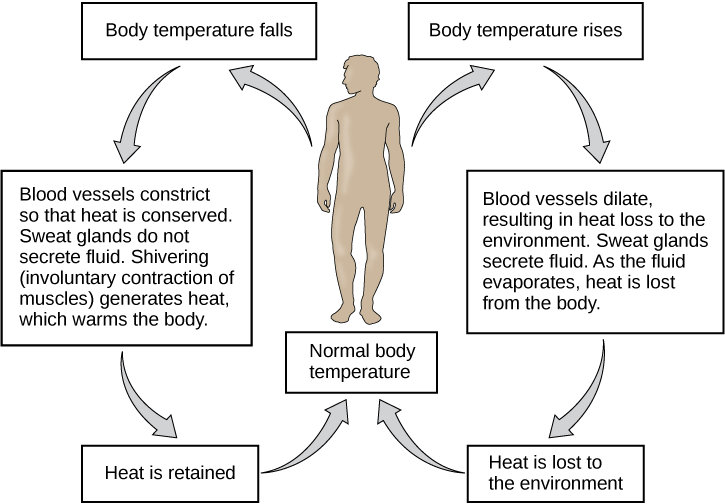
- Thermoregulation: The integumentary system helps to change body temperature. See Figure 5.1[2] for an illustration of thermoregulation. Thermoregulation is achieved by performing the following functions:
- Body temperature is decreased by the following actions:
- Sweating releases heat. Convection (air moving across the sweaty skin) lifts heat off the skin.
- Blood vessels in the skin are dilated to move warm blood near to the surface of the body to offload heat.
- Body temperature is increased by the following actions:
- Shivering occurs, with muscle contractions producing heat.
- Blood vessels in the skin are constricted to keep warm blood deep within the body and maintain a higher core body temperature.
- Body temperature is decreased by the following actions:
- Vitamin D Production: The skin makes vitamin D when it is exposed to UV radiation. The liver and kidneys work with the skin to produce the active form of vitamin D, which is needed for the body to absorb calcium and phosphorus from the foods that you eat.
- Betts, J. G., Young, K. A., Wise, J. A., Johnson, E., Poe, B., Kruse, D. H., Korol, O., Johnson, J. E., Womble, M., & DeSaix, P. (2022). Anatomy and physiology 2e. OpenStax. https://openstax.org/books/anatomy-and-physiology-2e/pages/1-introduction ↵
- “Figure_33_03_04” by CNX OpenStax is licensed under CC BY 4.0 ↵
definition
A condition in which the body loses more water than it takes in, affecting skin elasticity.
The transfer of heat through the movement of air or liquid around the skin.

